
What is Algorand? Another crypto asset pledging to solve the scalability trilemma and unseat Ethereum’s reign of power?
The Algorand platform is no small fish. Founded by one of the brightest minds in cryptography and establishing itself as the official blockchain partner of FIFA, Algorand appears to have fingers in all the right pies. Even SEC chair Gary Gensler, who generally wants to see the crypto industry collapse, has firmly supported ALGO.
Despite all these high-profile connections, the Algorand network has struggled to reach the adoption levels that ALGO holders would hope for. To give you an idea, Algorand TVL is lower than both Fantom and Kava, two altcoin competitors with lower market caps and fewer resources.
Sponsored
On paper, the Algorand protocol has everything it needs to be a high-performing, popular blockchain. Why does the data not match the potential?
Table of contents
What is Algorand (ALGO)?
Algorand (ALGO) is the native cryptocurrency of a Layer One blockchain network aiming to redefine the boundaries of blockchain technology. Founded by revered MIT professor and cryptography pioneer Silvio Micali, Algorand is a permissionless, open-source platform anyone can build upon.

Like most traditional blockchain platforms, Algorand was designed with a unique trifecta in mind: speed, security, and decentralization. It’s a platform that doesn’t just aim to be another horse in the race but seeks to address Vitalik Buterin’s iconic Blockchain Trilemma, an obstacle for many blockchain networks.
Sponsored
At its core, Algorand is a payments-focused network boasting rapid transactions and a strong emphasis on achieving near-instant finality. This means it’s capable of processing over 1,000 transactions per second (TPS) and performing transaction finality in less than five seconds.
How Does Algorand Work?
Algorand operates on a unique framework that differentiates it from traditional blockchain networks. The Algorand protocol’s beating heart and main unique feature is the Pure Proof-of-Stake (PPoS) consensus mechanism, a highly democratized version of the PoS model.
This novel consensus protocol allows any holder of the ALGO digital currency to participate in the network’s operation, with only one ALGO coin needed to join in.
The Pure Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism functions through a two-phase block production process: proposing and voting.
Anyone on the Algorand network can participate in these procedures by staking ALGO coins and creating a valid participation key to become a Participation Node. These nodes are managed by Relay Nodes, which share messages among Participation Nodes but do not directly participate in proposing or voting.
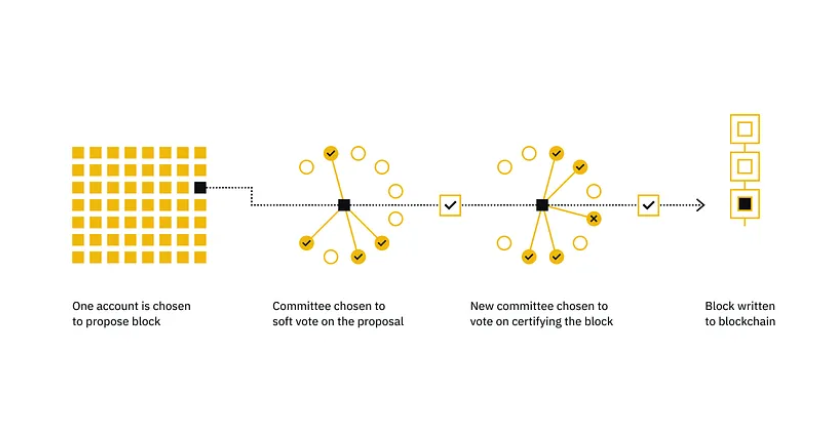
Starting with the proposal phase, a block leader is selected to propose the current block. This selection is made via Algorand’s verifiable random function (VRF), a mechanism that randomly selects nodes but with a weighting based on the size of their respective stakes.
Following the proposal, the voting stage begins. Participation Nodes are randomly elected to a committee responsible for ensuring no double-spend, overspend, or other problem has occurred in the current block.
If the committee agrees that all is well, the block is added to the blockchain. If malicious activity is detected, the Algorand network enters recovery mode, discards the block, and elects a new block leader.
What Makes Algorand Special?
Algorand stands out in the crowded field of blockchain technologies due to several unique features and innovations. Most importantly, Algorand is fast and affordable. The network is capable of processing around 1,000 transactions per second, near-instant transaction finality, and an average gas fee of $0.0001 USD.
Next up, Algorand’s two-tiered blockchain structure is certainly creative. The base layer supports smart contracts, asset creation, and atomic swaps between assets, ensuring security and compatibility.
The second layer, reserved for more complex smart contracts and dApp development, allows Algorand to process transactions efficiently. This network separation enables Algorand to handle the requirements of widespread global usage and a variety of use cases.
In a world where Bitcoin’s (BTC) carbon footprint goes toe-to-toe with that of a small nation, Algorand’s commitment to sustainability is a breath of fresh air. According to the Algorand Foundation, the network is carbon-negative thanks to its low energy requirements and carbon offsetting commitments.
What Can I Do on the Algorand Blockchain?
The Algorand blockchain is a versatile platform that supports a wide range of activities and applications. From decentralized finance (DeFi) to non-fungible tokens (NFTs), Algorand provides a robust and scalable infrastructure for various use cases.
Algorand DeFi
Decentralized finance, or DeFi, is one of the most prominent applications on the Algorand blockchain. Algorand’s high transaction speeds and low fees make it an attractive platform for DeFi applications.
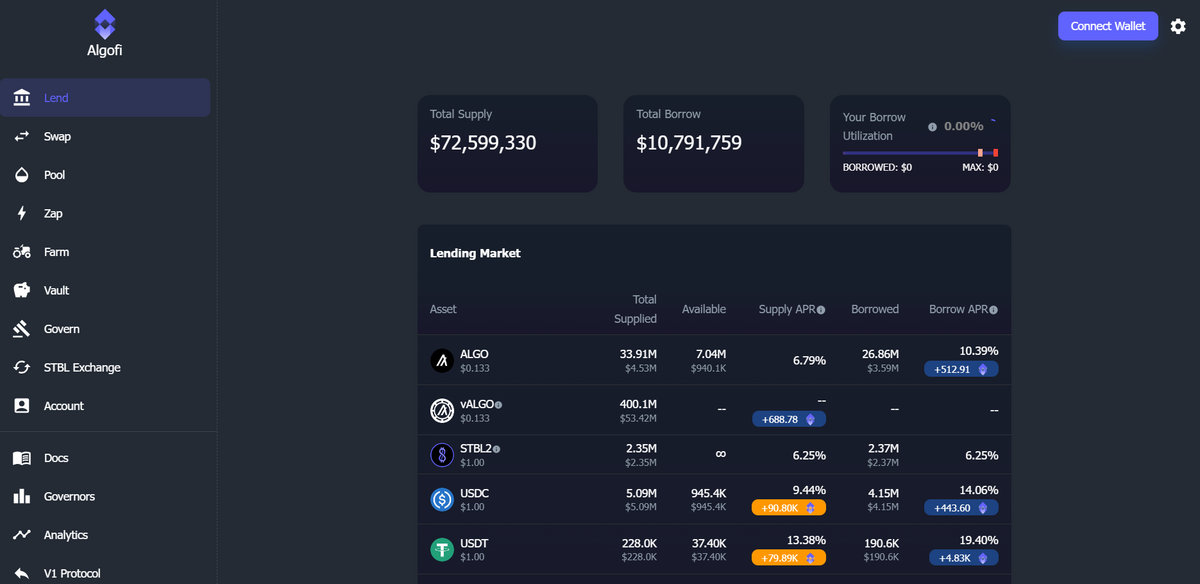
Using dApps like AlgoFi, the Algorand community can participate in lending and borrowing, yield farming, and trading stablecoins like USDT on a decentralized exchange. The platform’s smart contract capabilities support the creation of complex financial instruments and services that operate without intermediaries.
On top of that, applications like Lofty help people invest in real-world assets like fractionalized property in a transparent, on-chain environment.
Algorand NFTs
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) have taken the digital art and collectibles world by storm, and Algorand should be well-positioned to support this trend. The Algorand Standard Asset (ASA) protocol allows developers to create new digital assets, like NFTs, within the Algorand ecosystem.
However, even with Algorand’s low transaction fees, the ecosystem’s NFT culture hasn’t built much of an identity. NFT trading volume on the network is low, especially when compared to other networks like Cardano (ADA) or Solana (SOL).
I quickly poked around some of the collections available on Rand Gallery, the network’s leading NFT marketplace. The range and quality of NFTs available left a lot to be desired, to say the least.
The Birth of ALGO: Algorand History
The story of Algorand is a tale of innovation and ambition in the world of blockchain technology. The brainchild of Silvio Micali, a Turing Award-winning cryptographer and MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) professor, Algorand was born out of a desire to solve the Blockchain Trilemma. Sounds familiar, I know, but it’s a common problem.
Algorand’s launch was marked by an initial coin offering (ICO) in June 2019, which saw the creation and release of its ALGO tokens. The Algorand platform quickly gained attention for its innovative approach and potential to disrupt the crypto space.
However, the journey has not been without its challenges. In April 2023, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) declared that ALGO was an unregistered security, sparking debates within the crypto community.
Gary Gensler and the Algorand Blockchain
Gary Gensler, the Chairman of the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), has a notable connection with Algorand. When he was a professor at MIT’s Sloan School of Management, Gensler declared that Algorand was a “great technology” and that popular real-world apps like Uber or Lyft could be built on it.
It seems ironic that Gensler and the SEC would label ALGO as an unregistered security just four years later. Pockets of the crypto community have condemned Gensler for ‘shilling’ ALGO, which is down over 90% in USD value since he sang its praises in 2019.
Algorand vs. Ethereum (ETH)
Algorand and Ethereum are both influential platforms in the blockchain space, but they differ significantly in their design, functionality, and goals.
Ethereum, launched in 2015, is the home of smart contract functionality and decentralized applications (dApps). Ethereum’s network has been the birthplace of many significant developments in the crypto space, including DeFi and NFTs. That said, it faces challenges related to scalability, high gas fees, and network congestion.
| Ethereum | Algorand | |
| Transactions Per Second | 15-30 | 1,000 |
| Transaction Finality | ~15 minutes | ~5 seconds |
| Average Transaction Fee | $10-$80 (depending on network congestion) | $0.0001 |
On the other hand, Algorand, launched in 2019, offers many of the same tools and features. It’s a smart contract compatible network, with plenty of room for innovative defi applications and wider world use cases. Algorand’s design makes it faster and more affordable than Ethereum.
While Algorand is arguably the better platform, it simply cannot compete with Ethereum’s network effect. Ethereum is the center of innovation in the crypto space, with a far wider variety of tools and applications than Algorand can offer at this time. That being said, Ethereum’s ongoing issues leave Algorand plenty of room to catch up and compete for Layer One dominance.
What’s Holding Algorand Back?
Remember earlier when I mentioned that networks like Fantom and Kava enjoy higher usage rates and TVL than Algorand, despite Algorand’s superior resources and connections? This is most likely due to Algorand’s inoperability with other networks.
Both Fantom and Kava are EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) compatible, meaning it’s much easier to port Ethereum-based applications over to these networks. This makes building essential DeFi tools and creating a thriving ecosystem a faster and simpler process.
In a bid to make the network EVM compatible, the Algorand Foundation launched a $10M USD grant incentivizing developers to build a solution. While MilkoMeda has created a platform that brings EVM compatibility to Algorand, the onboarding process is still quite convoluted, discouraging Ethereum users from bridging over to the network.
Moreover, the Layer One race is competitive. Let’s face it, Algorand’s 1,000 TPS might seem impressive compared to Ethereum, but compared to modern networks like Aptos (APT) or Solana, which theoretically pump out 100,000+ TPS, Algorand still has some catching up to do.
Algorand Cryptocurrency Pros and Cons
Like any technology, Algorand has its own advantages and disadvantages. Here’s a look at some of the pros and cons of the Algorand cryptocurrency:
Pros
- Speed and Scalability – Algorand is a performant network, supporting fast transactions and high throughput.
- Low Transaction Fees – Algorand’s design allows for low transaction fees, making it an attractive platform for developers and users alike.
- Democratized Participation – The protocol’s unique consensus mechanism allows any holder of the ALGO cryptocurrency to participate in the network’s operation, even if they only hold 1 ALGO coin.
- Energy Efficiency – Unlike many other blockchain networks that consume huge amounts of energy, Algorand is designed with sustainability in mind.
- Strong Team and Real-World Connections – Algorand was founded by Silvio Macali, one of the world’s leading cryptographers, and has made impressive strategic partnerships with global brands like FIFA.
Cons
- Regulatory Uncertainty – The SEC has declared that ALGO is an unregistered security, casting doubt on its future.
- Smaller Ecosystem – Algorand suffers from low user numbers and low TVL, making it unattractive for developers looking to deploy applications.
- Strong competition – Algorand is going head-to-head against some of the largest projects in the space, including Ethereum, Solana, and Cardano.
On the Flipside
- As more blockchains seek energy-efficient solutions, networks that are sustainable by design, like Algorand, have a distinct advantage over platforms that must adapt their existing structure.
Why This Matters
Algorand is one of the larger Layer One networks in the industry and shows plenty of promise. If Algorand succeeds in attracting more users and on-chain value, there’s no reason why it cannot compete with other top networks.
FAQs
You can buy Algorand on top crypto exchanges like Binance and Coinbase.
Algorand is a blockchain network that supports peer-to-peer payments, smart contract development, and decentralized applications.
Algorand’s top competitors are Ethereum, Solana, and Cardano.
If Algorand were to reach $100, the market cap of ALGO would be worth over $700B. This valuation would make ALGO larger than Bitcoin at current prices.
