
As if the labyrinthine world of blockchain wasn’t already complicated enough, the scores of crypto abbreviations can make your first steps into Web3 even more confusing. The sheer amount of crypto culture quips and memes is staggering, but learning them is necessary for everyone’s cryptocurrency education.
From the classics like ‘HODL’ and ‘DYOR’, all the way through to specific consensus mechanisms like PoW and PoS, the crypto space is full of short-hand crypto acronyms. This article will bring you up to speed on the most common crypto abbreviations you can expect to encounter in this weird and wonderful corner of the internet.
Common Crypto Acronyms
Our crypto abbreviations list is divided into three main categories: technical, financial, and cultural.
Sponsored
Because every sub-niche in the digital asset industry has specific acronyms, the list of possible abbreviations is almost endless. But don’t worry, our list of essentials will give you everything you need to know to confidently navigate the crypto market!
Technical Cryptocurrency Abbreviations
Technical crypto abbreviations refer to anything related to how blockchain networks function. They include everything from mining equipment to token standards. Knowing your way around technical terms is helpful when researching new protocols in the blockchain industry.
- 2FA – 2 Factor Authentication: 2FA adds an extra layer of security to your accounts. An example of 2-factor authentication is verifying a six-digit code that gets sent to your email address before withdrawing crypto from an exchange.
- ASIC – Application-Specific Integrated Circuits: ASICs are powerful computer chips in Bitcoin (BTC) mining rigs. They’re generally optimized for successful mining and are more powerful than GPUs.
- BFA – Brute Force Attack: A BFA is a cyber-attack where a hacker tries to guess a password, or seed phrase, by testing possible outcomes as quickly as possible.
- BFT – Byzantine Fault Tolerance: BFT is a standard that ensures blockchain networks are able to continue functioning correctly, even when some nodes have failed or acted maliciously.
- CPU – Central Processing Unit: CPUs are one of the most critical pieces of hardware making up a computer.
- DAG – Directed Acyclic Graph: A DAG is another type of distributed ledger that stores crypto assets and supports smart contract development, similar to a blockchain.
- dApp – Decentralized application: dApps are products and tools built on the blockchain using smart contracts. They are trustless and permissionless, meaning anyone can use them at any time.
- DEV – Developer: A developer is a professional who builds blockchain applications or infrastructure.
- EIP – Ethereum Improvement Proposal: An EIP is a suggestion made from within the Ethereum (ETH) community regarding how the network can be improved. Ether holders can vote on whether the improvement is implemented through Ethereum’s decentralized on-chain governance.
- EVM – Ethereum Virtual Machine: The EVM is a computational engine and environment that stores data of all accounts on the network and enables developers to code smart contracts and deploy dApps.
- ERC-20 – Ethereum Request for Command 20: ERC 20 refers to the set of rules and conditions for typical cryptocurrency tokens on the Ethereum blockchain.
- ERC-721 – Ethereum Request for Command 721: Similar to ERC 20, ERC 721 is a standard of rules and conditions for most non-fungible tokens on the Ethereum network.
- GPU – Graphics Processing Unit: Before shifting to more powerful ASIC mining rigs, many Bitcoin and Ethereum mining operations were powered by GPUs.
- IPFS – Interplanetary File System: The IPFS is a distributed data storage system and transfer network. Any computer anywhere in the world can access the IPFS to serve and host data.
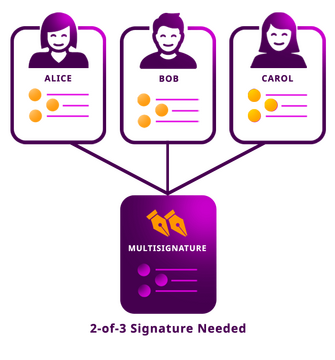
- Multi-Sig – Multi-Signature: A Multi-sig is a security feature where several people must sign a crypto wallet’s transaction before it is executed. It’s generally used within crypto project teams to stop individual members from using funds without the agreement of other team members.
- NFT – Non-fungible token: An NFT is a digital asset that is completely unique. One of the most common use cases of NFTs is to prove ownership of digital art.
- PoS – Proof of Stake: PoS is a consensus mechanism that secures blockchains and produces new blocks. Validators commit crypto assets to the network in exchange for rewards proportionately distributed based on their stake in the network.
- PoW – Proof of Work: PoW is an algorithm that helps a blockchain, like Bitcoin, reach consensus and create new blocks. Miners solve complex computational equations to earn the right to produce new blocks and earn crypto rewards.
- SATS – Satoshi: Named after the Bitcoin creator, SATs are a denomination of BTC. There are 100,000,000 SATs in one Bitcoin.
- SC – Smart contract: A Smart contract is a line of code that automatically executes programs and functions when certain conditions are met.
- TPS – Transactions Per Second – TPS is a metric that quantifies how many transactions a blockchain network can process in one second. The higher the TPS, the faster the network.
- TX – Transaction: A Tx refers to an on-chain event, like transferring funds to another wallet or trading tokens on a decentralized exchange through a smart contract.
Financial Abbreviations
The next category of crypto abbreviations is a bit less niche and easier to understand, even if you have no blockchain background. Some of these abbreviations also apply to financial institutions and financial services outside the crypto market.
- ATH and ATL – All-time high/low: An ATH/ATL refers to a particular asset’s highest or lowest recorded price.
- ALT – Altcoin: When discussing digital currencies in the crypto market, ALTs refers to any coin that isn’t Bitcoin. Some crypto enthusiasts would argue that ETH has become so dominant that it’s no longer considered an altcoin.
- CEX – Centralized Exchange: Binance and Coinbase are centralized exchanges, they provide a marketplace where traders and investors can buy and sell crypto assets through a company governed by a central authority.
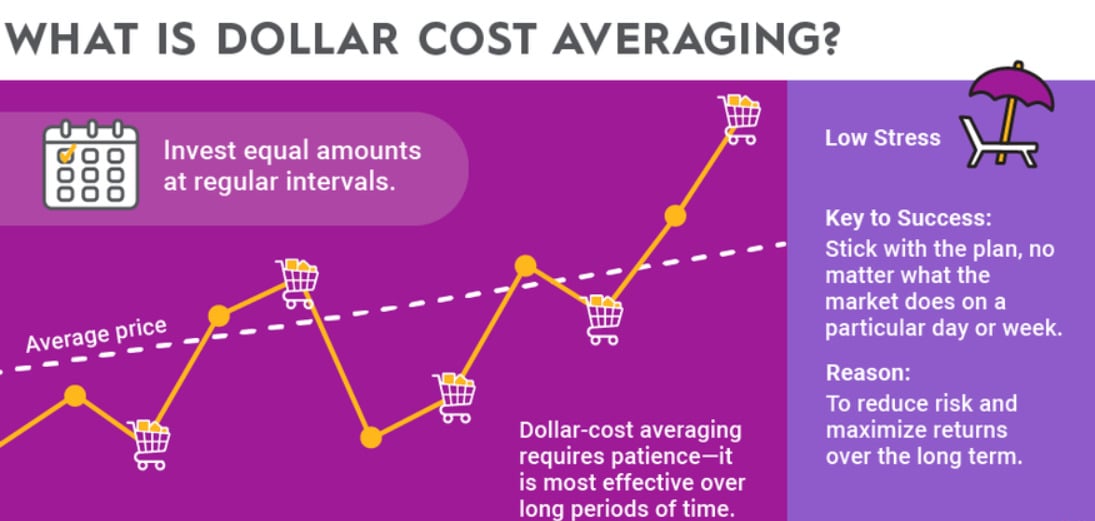
- DCA – Dollar Cost Average: Instead of trying to time the market and make big investments all in one go, dollar cost averaging means buying smaller amounts over a designated period. Many investors consider it a way to accumulate an asset without being too affected by market volatility.
- DeFi – Decentralized finance: DeFi is one of the cornerstones of the blockchain revolution and perhaps the most important use case of the technology. DeFi is the name given to financial services, products, and tools built on the blockchain and accessible to all.
- DEX – Decentralized Exchange: A DEX is a DeFi application where users trade cryptocurrencies using smart contracts. This avoids relying on a central authority like Binance to manage the transaction. On a DEX, users are fully anonymous and have full control of their funds.
- DLT – Distributed Ledger Technology: DLT is a broad umbrella term that covers systems, like blockchain and DAG, used to create and manage a decentralized, public ledger of transactions.
- ETF – Exchange-Traded Fund: An ETF is an index fund comprised of a basket of different assets.
- FA – Fundamental Analysis: FA is a market research technique where traders explore upcoming events and developments in a crypto projects roadmap to determine whether they think the price will go up or down.
- FIAT – Also called ‘real money,’ FIAT means any government-issued currency like US dollars or euros.
- ICO – Initial Coin Offering – An ICO is a fundraising event hosted by new crypto projects. During an initial coin offering, the crypto company sells tokens to investors at a set price before the token is listed on a public market.
- KYC – Know Your Customer: KYC is a process that identifies you to a central authority, giving you access to their products and services.
- MCAP or MC – Market Cap: Market Cap is a way of determining the perceived total value of a particular cryptocurrency. To find a coin’s market cap, multiply the coin’s price by the number of coins in circulation.
- OTC – Over The Counter: In an OTC deal, holders trade digital assets directly to another party instead of through an exchange. This is usually done to avoid paying trading fees.
- PnL – Profit and Loss: PnL measures how successful someone’s trading history or investment portfolio is.
- PvP – Player vs. Player: A PvP market suggests that the market is a zero-sum game. Where there is a winning trade, someone has made a losing trade.
- Stables – Stablecoins: Stablecoins are cryptocurrency assets pegged to the value of fiat currencies.
- TA – Technical Analysis: Skilled traders read price charts and follow patterns and indicators in an asset’s price history to determine whether it will go up or down. This research method is called technical analysis.
- TVL – Total Value Locked: TVL is a popular metric to determine whether a blockchain network is valuable. It calculates the amount of funds stored in DeFi apps at any moment.
Crypto Community Culture Abbreviations
If you’ve ever spent time in a crypto Telegram channel, you’ve probably seen or heard most of these acronyms hundreds of times. Crypto culture relies on these shorthand abbreviations to keep things light and fun. These crypto abbreviations are often intentional misspellings.
- AMA – Ask Me Anything: In an AMA, project founders go before their community to answer any questions about their project and its development, almost like an open interview or press conference.
- BTD – Buy The Dip: BTD is a common imperative amongst the crypto community. As the name suggests, it encourages people to purchase tokens and coins in a downtrend.
- BUIDL – Frequently used by Changpeng ‘CZ’ Zhao, ‘BUIDL’ is a rallying call to ignore the noise and volatility and build crypto products and services.
- CG & CMC – Coingecko & CoinMarketCap: These two popular sites provide up-to-date information on cryptocurrency prices.
- CT – Crypto Twitter: CT is a social environment where crypto enthusiasts share ideas and opinions on the crypto market. It is also a source of breaking news and is used to gauge market sentiment.
- DAO – Decentralized Autonomous Organization: A DAO is a self-governing group with aligned goals. DAOs have no central authority and typically use on-chain voting protocols to make crucial decisions.
- DC – Discord: Discord is a common social media platform that crypto projects use to share information with their community.
- DYOR – Do Your Own Research: To DYOR is to conduct thorough due diligence in a crypto asset before investing or opening a trade.
- ELI5 – Explain Like I’m 5: The crypto space can sometimes be complicated, so an ELI5 is used to break down complex topics into simple explanations.
- FOMO – Fear of Missing Out: FOMO is what you feel when you see the market going green and taking off without you. Human greed kicks in, making traders buy crypto assets because they don’t want to miss the pump.
- FUD – Fear, Uncertainty, and Doubt: Unfortunately, FUD is a big part of the crypto market. FUD refers to negative sentiment or comments made directly to a specific project in an attempt to push prices down. While FUD is often made using baseless claims, it’s essential to be objective. Many of the early comments predicting the downfall of Terra Luna were dismissed as FUD before the ecosystem crashed.
- GM – Good Morning: GM is the greeting of choice amongst crypto enthusiasts.
- HODL – Hold On for Dear Life: To HODL crypto is never to sell, regardless of whatever is happening in the market.

- NGMI – Not Gonna Make It: NGMI is a dismissive term used to describe someone who won’t succeed in crypto.
- PnD – Pump and Dump: A PnD is when the price of specific token spikes and drops sharply over a short-term timeframe.
- REKT – Wrecked: Being REKT refers to taking a heavy loss on a trade or investment. Some crypto circles might also say ‘down bad’.
- TG – Telegram: Alongside Discord, TG is a popular messaging platform where crypto communities and projects share information, ideas, and opinions.
- WAGMI – We’re All Gonna Make It: WAGMI is a rallying call within the crypto community. It suggests that everyone who’s invested in a certain project will be successful.
On the Flipside
- It’s important not to be led astray by trendy catchphrases and inspiring abbreviations in the crypto market. WAGMI is a perfect example of this. The crypto market is a competitive, PvP environment. If you’ve made a winning trade, that means that someone, somewhere, has made a losing trade.
- Avoid cult-like euphoric behavior. Always DYOR.
Why This Matters
Knowing crypto abbreviations by heart helps you to navigate the blockchain industry more efficiently and save time. They’re also an integral part of crypto culture and help you feel like you’re part of a community.
FAQs
Like regular slang, crypto slang is a subset of language used within the crypto community.
In crypto, CT means Crypto Twitter. Crypto Twitter is the dominant social network for following events and updates in the crypto industry.
OG is an acronym for Original Gangster in the crypto space. It refers to someone who has been in the industry for a long time.
LFG means ‘Let’s F**king Go’. Crypto enthusiasts generally say LFG when they’re excited about a particular project.
Crypto symbols like BTC and ETH are short-form tickers that represent the coin on trading platforms. These are sometimes called cashtags.
