
In the eyes of cryptocurrency purists, Cardano coin is the perfect blockchain. The Cardano network ticks all the boxes to secure, scalable, and boasting levels of decentralization that its rivals can only dream of. It goes a long way toward solving Vitalik Buterin’s blockchain trilemma.
Despite its potential, Cardano is still far from its final form. Backed by years of theoretical, peer-reviewed research, Cardano’s slow delivery has caused many complaints. At the same time, comparatively low network usage to other Layer One blockchains has left ADA with a spooky moniker.
As we all know, good things take time, but how long is too long? Is Cardano truly the visionary blockchain that Charles Hoskinson, IOHK, and the Cardano Foundation have promised, or does the ‘Ghost Chain’ deserve its name?
Table of Contents
What Is Cardano Coin?

Cardano is a sophisticated Layer One blockchain platform. Built on a foundation of peer-reviewed research and evidence-based methods, this groundbreaking open-source ecosystem has long held a position as one of the largest cryptocurrencies in the blockchain industry.
Sponsored
Launched in 2017 by former Ethereum (ETH) co-founder Charles Hoskinson, this proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchain platform has been meticulously designed to offer unparalleled security, scalability, and sustainability. The network’s native token, ADA, was named after Ada Lovelace, a 19th-century English mathematician.
Cardano coin boasts a noble vision that even Satoshi Nakamoto, the founder of Bitcoin (BTC), would be proud of. Aiming to redistribute power from centralized systems back to the people, Cardano is an enabling force for positive change, striving to create a more secure, transparent, and equitable world.
How Does Cardano Work?
Peeling back the layers of Cardano’s complex architecture, we find a symphony of sophisticated technologies working harmoniously.
Sponsored
Cardano operates on a Proof-of-Stake mechanism, a timely departure from the energy-intensive Proof-of-Work systems that have long been the industry standard. This makes the network more energy-efficient, democratizes the transaction validation process, and distributes network governance.
ADA Holders can deposit their cherished tokens into Cardano community-operated staking pools to secure the network and produce new blocks. As a reward for their commitment to decentralization and network growth, ADA token stakers earn crypto rewards through Ouroborus, Cardano’s innovative consensus model.
Ouroborous – Cardano’s Unique Consensus Mechanism
Named after the Greek legend of the snake eating its own tail, Ouroboros is the first peer-reviewed, verifiably secure blockchain protocol. It allows the network to achieve consensus without relying on a central authority, redistributing power back to the community. But it does so with an unprecedented level of security and efficiency.
How does it accomplish this feat? The Ouroboros algorithm divides time into epochs, which are further divided into slots. Slot leaders are chosen based on the number of ADA tokens they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral.
These leaders run nodes that validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. The process is not only democratic but also ensures that the system remains decentralized and secure.
Cardano boasts one of the highest Nakamoto Coefficiency scores in the Web3 world, proving its high standard of decentralized network security.
But Ouroboros doesn’t stop there. It’s continuously evolving, propelled by a vision for more secure and transparent global payment systems and a means to redistribute power more equitably. But what good is distributed power if it isn’t scalable enough to support mass adoption?
That’s where Hydra comes in.
Hydra

Designed to supercharge the network’s capabilities, Hydra tackles one of the most pressing issues in blockchain technology: scalability. As blockchain networks grow, they often become victims of their own success, struggling to handle increased traffic, which leads to slower transaction times and higher fees. Hydra solves this problem by increasing transaction speed through low latency and high throughput, all while minimizing transaction costs.
How does Hydra achieve this? It employs a technique known as “isomorphic state channels,” allowing transactions to occur off the main chain, thereby reducing the load on the network.
These channels can process transactions independently, and once completed, the final state is uploaded back onto the main chain. This speeds up individual transactions and allows for more transactions to be processed simultaneously.
Beyond boosting network scalability, Hydra also opens the door to more complex and resource-intensive operations, such as smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps), without bogging down the network.
What Can I Do on Cardano?
Technical jargon and saucy promises are all well and good. But what can one actually do on Cardano’s settlement layer? Is it merely a smart contract platform for financial transactions, or does it offer something more?
DeFi
Cardano’s secure and scalable infrastructure makes it an ideal platform for decentralized finance. In fact, Cardano’s emerging DeFi scene is undergoing something of a renaissance, with the network recording all-time high levels of TVL (Total Value Locked) in terms of ADA month on month throughout 2023.
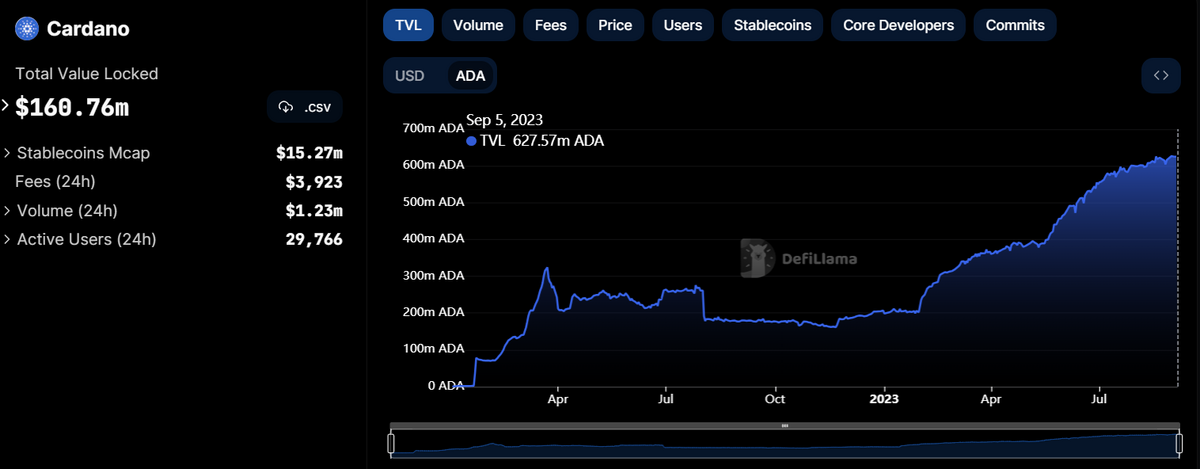
From decentralized exchanges like MinSwap to permissionless money markets and the blockchain’s native algorithmic stablecoin, DJED, Cardano dApp users are spoilt for choice. Committed to accessibility, Cardano’s financial systems are open, transparent, and accessible to everyone with a wallet and internet connection.
Not wanting to be outdone by other chains, Cardano even boasts its own range of popular meme coins, like SNEK (SNEK).
NFTs
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) have taken the digital world by storm, and Cardano coin certainly hasn’t been left behind. Its energy-efficient proof-of-stake mechanism makes it an attractive platform for minting NFTs. It allows artists and creators to tokenize their work without the environmental guilt associated with other blockchains.
Cardano’s NFT ecosystem is smaller than competitors like Ethereum and Solana (SOL). But that doesn’t mean it doesn’t have plenty to offer the avid collector. NFT Marketplaces like JPG Store are the bustling heart of NFT culture on Cardano, with a wide range of quirky characters and unique 1/1 art pieces.
Education
While the buzz around blockchain often centers on finance and digital assets, Cardano is setting its sights higher, aiming to bring about transformative change in sectors as vital as education. While other blockchains worry about gas fees, Cardano is busy supporting a database of over five million students in Ethiopia.
Cardano’s secure and transparent ledger is ideal for storing and verifying educational credentials. In a world where qualifications are increasingly scrutinized, Cardano offers a tamper-proof system where academic achievements can be easily verified, reducing fraud and increasing trust.
But it goes beyond just storing degrees and certificates; it opens up the possibility for a more equitable educational system where your credentials and achievements are universally recognized, irrespective of where you studied.
From the Lab to the Blockchain: Cardano’s History
Cardano’s history is certainly a compelling narrative. How did Cardano evolve from a theoretical concept to a transformative force in the blockchain landscape?
Cardano was born out of a desire to address the limitations of existing blockchain platforms, primarily scalability, security, and sustainability.
Founded in 2017 by Charles Hoskinson and Emurgo, Cardano was far from rushed. The proof-of-stake was meticulously designed based on peer-reviewed research and developed through evidence-based methods. Taking things one step further, Cardano was coded using its own dedicated programming languages, namely Plutus and Haskell.
This academic rigor sets Cardano coin apart from many other blockchain projects, which often prioritize speed over security or functionality over feasibility. Continuing the academic theme, each era of Cardano’s complex roadmap is named after historical figures like Shelley, Goguen, and Voltaire.

Every step corresponds to a new development vertical, whether decentralized staking, a network hard fork that introduces smart contract support, or network governance architecture.
Cardano vs Ethereum
As two of the top Layer One smart contract platforms in the crypto space, comparing Cardano and Ethereum is inevitable. Both platforms aim to offer decentralized applications and smart contracts, but their approaches are markedly different.
Ethereum, the pioneer in the field, has the first-mover advantage but is grappling with scalability and usage costs. It struggles with low transaction throughput and high gas fees, making it ill-equipped for mass adoption.
Cardano, on the other hand, was designed to address these very issues. Thanks to the Hydra Scaling solution and low transaction fees, Cardano is primed to receive more users.
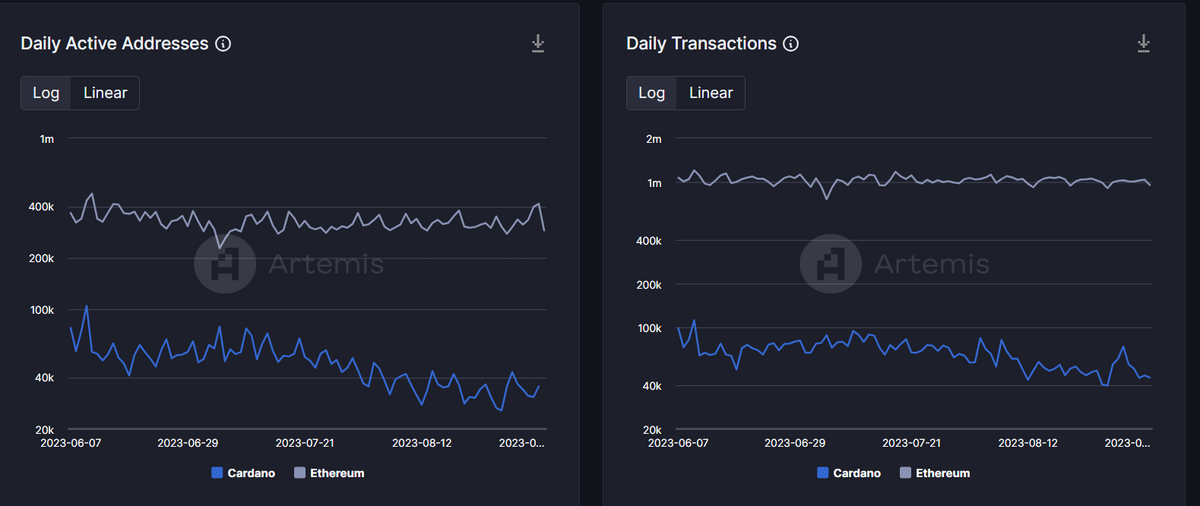
However, despite its arguably superior architecture, Cardano struggles to achieve the same dominance and network effect that Ethereum exerts over the market. According to data provided by Artemis and DeFiLlama, Ethereum is light years ahead of Cardano in terms of Daily Active Addresses, Daily Transactions, and network TVL.
Is Cardano Really a ‘Ghost Chain’?
Like oil to a naked flame, ‘Ghost Chain’ is a sensitive term for Cardano. As the name suggests, a ‘Ghost Chain’ is a blockchain with little activity.
Despite its technological promises, ‘Ghost Chains’ are like empty vaporware that lacks real-world applications or a vibrant community. Critics have hurled this term at Cardano, questioning its legitimacy and impact. But is this slander warranted?
The Cardano community, led by founder Charles Hoskinson, has defiantly refuted these claims, with evidence highlighting Cardano’s contributions to the blockchain space.
Let’s look at the facts. With over 72 million transactions, each representing a unique interaction and a thriving ecosystem of decentralized applications, Cardano is anything but a ghost town. The network has also enjoyed over six years of constant runtime, marking a testament to its durability and robustness.
The platform boasts impressive TVL statistics, which have surged by over 300% this year, showcasing the community’s confidence and engagement. On top of that, let’s not forget the 4.2 million ADA wallets in existence and the 22.6 billion ADA staked.
The final feather in the cap, Cardano was recently declared the number one developer platform in the Web 3 industry by Santiment, a leading blockchain analytics company.
Cardano Pros and Cons
Every novel technology has its own pros and cons, and the Cardano blockchain is no exception. Let’s delve into the pros and cons that make Cardano such a compelling subject of study and debate.
Pros
- Security – With its unique consensus mechanism, Ouroboros, Cardano offers watertight security, making it one of the most robust blockchain platforms.
- Scalability – Thanks to its Layer-2 solution, Hydra, Cardano can handle a large number of transactions simultaneously, making it highly scalable and efficient.
- Sustainability – Thanks to its proof-of-stake mechanism, Cardano is energy-efficient, offering a more sustainable alternative to energy-intensive proof-of-work blockchains.
- Decentralization – Cardano’s architecture ensures that power is distributed among its users, making it one of the most decentralized blockchain platforms.
- Academic Approach – With its focus on peer-reviewed research and evidence-based development, Cardano’s innovation is backed by scientific theory.
Cons
- Complexity – The very features that make Cardano innovative also make it complex, which could be a barrier to entry for some users and developers.
- Adoption – While Cardano has a strong community, it still lags in mainstream adoption, particularly compared to rivals like Ethereum and Bitcoin.
- Market Volatility – The crypto market hasn’t been kind to ADA, with over 80% of ADA holders currently down on investment.
- Slow Development – While commendable, Cardano’s meticulous approach to development means that it often takes longer to roll out new features.
On the Flipside
- Originally launched in 2017, Cardano is becoming one of the older altcoins in the crypto market alongside competitors like Ripple (XRP), Litecoin (LTC), and Dogecoin (DOGE). In an industry where shiny new things attract investors, ADA might struggle to see the same price action that it has in previous bull cycles.
Why This Matters
Cardano coin is one of the largest cryptocurrencies by market cap in the crypto space and boasts some of the industry’s most devout and passionate supporters. Understanding what Cardano is and how it works is crucial to staying up-to-date in the crypto market and making informed decisions.
FAQs
You can buy Cardano (ADA) on top crypto exchanges like Binance and Coinbase.
If Cardano reached $100 USD, it would have a market cap of $3.5 trillion. Given that this figure is larger than the market capitalization of the entire crypto industry, a $100 ADA is unlikely.
The maximum supply of ADA tokens is 45,000,000,000. This figure is not to be confused with ADA’s current total supply of 36,000,000,000.
The all-time high Cardano price was recorded on September 2, 2021. ADA price on this day was $3.10.
Cardano’s circulating supply is approximately 35B ADA tokens at the time of writing.
You can track the current price of Cardano, as well as other key statistics like 24-hour trading volume on sites like CoinMarketCap.
