
Suppose you’ve ever brought up cryptocurrency or the Web3 movement at the dinner table. In that case, you may have been crucified by uninformed relatives who told you that Bitcoin (BTC) and blockchain technology are an environmental catastrophe and that there’s no such thing as a ‘green crypto.’
Time to bust one of the biggest myths of the modern world. Blockchain isn’t bad for the environment. Even though people aren’t ready to hear it, some blockchain transactions use less energy than one Google search.
Admittedly yes, Bitcoin is far from an eco-friendly asset. But that doesn’t mean modern networks must be tarnished with the same brush. Many blockchain networks are actually carbon neutral, which is probably more than your local bank can say.
Sponsored
In this article, we’ll explore what it means to be a sustainable crypto project and see what top networks are doing in the fight against climate change and global warming.
Table of Contents
What Makes a Blockchain Environmentally Friendly?
Energy-intensive, legacy blockchains have often been likened to power-hungry monsters stamping gargantuan carbon footprints across our planet.
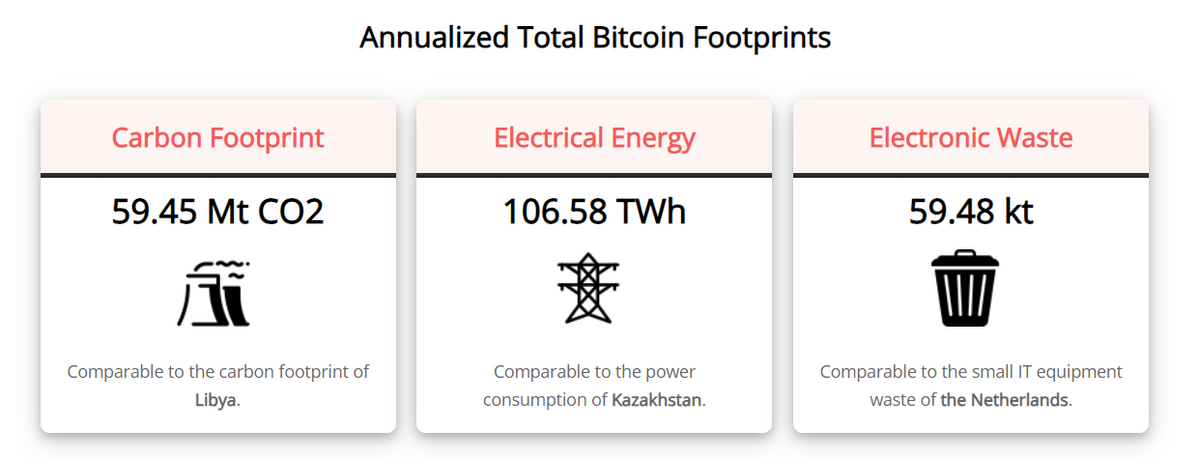
While Bitcoin has annual TWh stats that mirror a small nation and aren’t doing the planet any favors, the notion that all blockchains and crypto assets are environmentally destructive is simply ridiculous.
Sponsored
The industry has dozens of networks with a devout commitment to energy efficiency. For example, sustainable blockchains like Solana (SOL) and Cardano (ADA) require significantly less energy per transaction than older networks. This doesn’t just mean lower electricity bills from cryptocurrency mining or staking; it translates to a reduced demand on power grids and a decreased reliance on fossil fuels.
One of the most important features that impact blockchain energy consumption is its consensus mechanism. This is how transactions are verified and added to the network.
On top of the technical aspect, an environmentally conscious blockchain often has a broader sustainability vision. This could involve supporting renewable energy sources, carbon credits, and offsetting carbon emissions. We also need to consider the relative size of the network; smaller networks with low usage stats might have lower energy requirements but still be unproven when put under strain.
Proof-of-Work vs. Proof-of-Stake
Most green crypto debates boil down to which consensus mechanism is used to secure the network. While early Proof-of-Work blockchains like Bitcoin and pre-merge Ethereum (ETH) boast enormous electricity consumption, rates of modern Proof-of-Stake networks are tens of thousands of times more energy efficient.
Why is that? Let’s quickly recap the difference between PoW and PoS:
- Proof-of-Work (PoW) – Imagine a vast digital mine where countless crypto miners are tirelessly solving complex mathematical puzzles. The first to solve it gets to add a block to the blockchain and earns crypto rewards. The Bitcoin mining process demands massive computational power, which results in immense energy usage and a large carbon footprint.
- Proof-of-Stake (PoS) – In a PoS consensus, validator nodes are chosen to create blocks based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” or lock up as collateral. It’s akin to a digital lottery where your chances increase with the number of tickets (or coins) you hold. The beauty of PoS? It drastically reduces the need for computational power, making it a more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly alternative.
While some cryptocurrency purists argue that PoW is a more secure consensus method, PoS is undoubtedly more energy efficient. When Ethereum changed from PoW to PoS during The Merge, network energy consumption was reduced by 99.9%, and it uses less energy per year than PayPal.
Top Green Cryptocurrencies
From harnessing renewable energy to adopting energy-efficient consensus mechanisms and reducing their environmental impact, these digital assets are redefining what it means to be a cryptocurrency today.
Which eco-friendly trailblazers are leading the charge to a sustainable future?
1. Solana (SOL)
In an unsurprising twist, the top green crypto has a greenish logo and branding. At its core, Solana uses a unique consensus mechanism known as Proof-of-History (PoH), which is a spin on the existing PoS model.
This innovative approach allows for quicker validations without the need for massive energy consumption. Think of it as a chronological proof system, ensuring every transaction’s sequence without the back-and-forth communication typically seen in other blockchains.
While Anatoly Yakovenko’s blockchain actively supports collaborations with renewable energy providers and carbon offset programs, the network’s minuscule energy-consumption stats make it stand head and shoulders over its rivals.
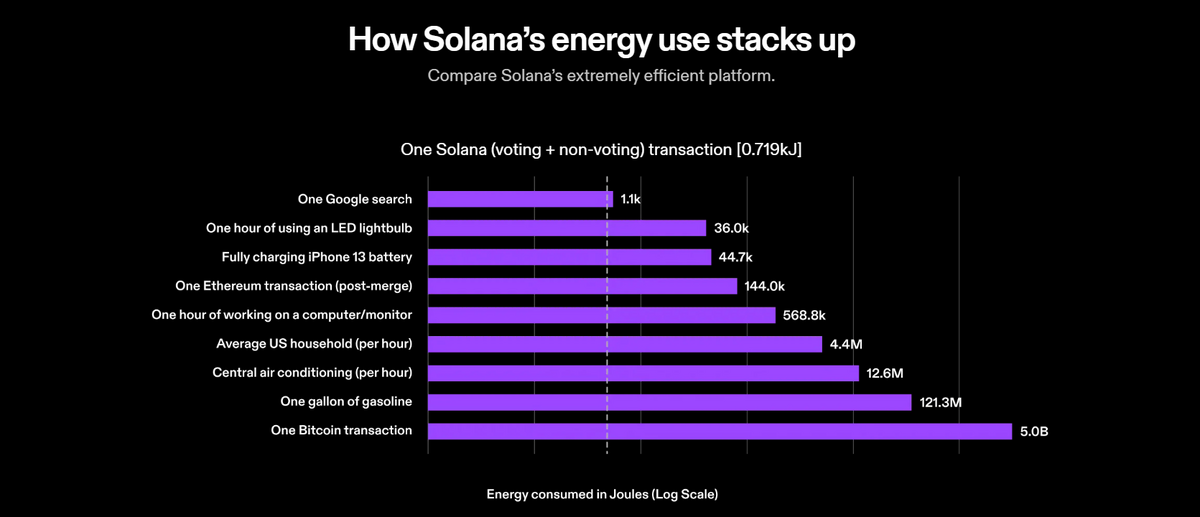
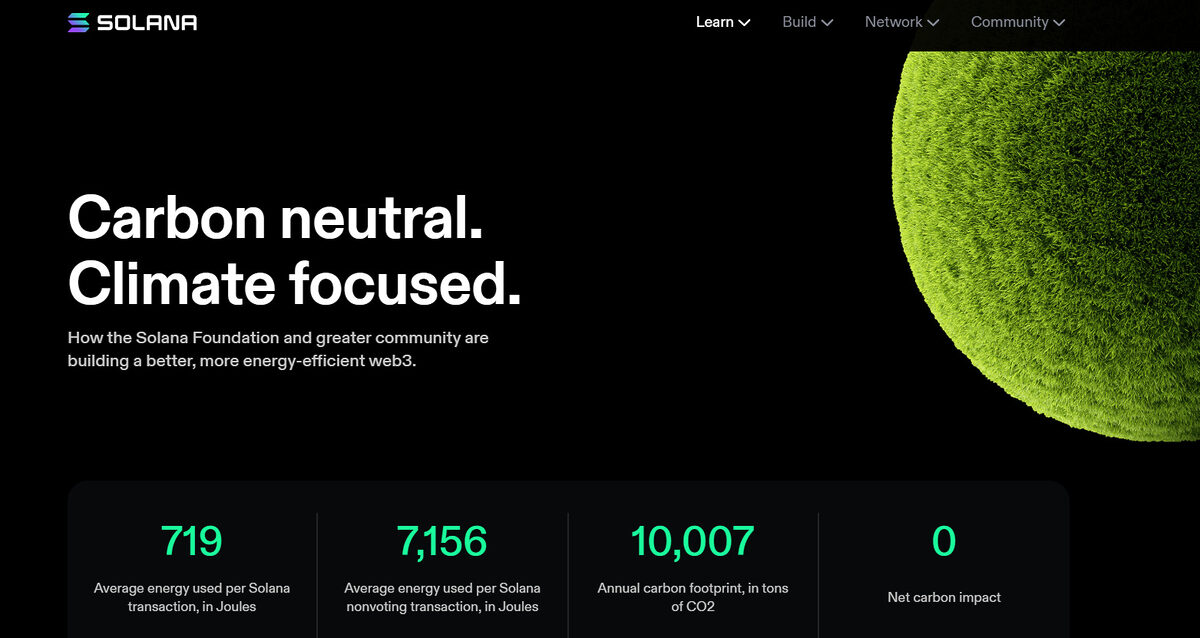
According to the Solana Foundation, one Solana transaction uses around 719 kilojoules (kJ). That’s less than the energy required to perform a single Google search.
When you stop and think about it, it’s wild that you can send $1M USD instantly across international borders to anyone using less electricity than a humble Google search. Yet, people still think that digital currency and NFTs are bad for the environment.
Key Points
- Consensus Mechanism: Proof-of-History (PoS variant)
- kWh per transaction: 0.00051 kWh
- Carbon Neutral: Yes
2. Hedera Hashgraph (HBAR)

Something of a wildcard in the green crypto space, Hedera (HBAR) operates on a unique consensus algorithm known as the hashgraph. This approach offers rapid transaction speeds and low energy requirements.
But Hedera’s eco-journey doesn’t stop at its consensus mechanism. Working in collaboration with the Crypto Climate Accord, Hedera is fully carbon neutral and has pledged to go further. Hedera is set on going carbon negative through carbon offsetting and credit programs.
A recent study by the University College of London Blockchain Centre found that the average Hedera transaction used only 0.000003 kWh of electricity, arguably making it the most energy-efficient blockchain. However, given that the Hedera network is considerably smaller and sees less smart contract activity than networks like Solana and Cardano, it doesn’t quite have the usage to warrant the top spot.
Key Points
- Consensus Mechanism: Hashgraph, Tangle
- kWh per transaction: 0.000003 kWh
- Carbon Neutral: Not currently, aims for Carbon negativity in the future.
3. Algorand (ALGO)

Founded by the renowned cryptographer Silvio Micali, Algorand (ALGO) wasn’t just built to challenge the status quo; it was designed from the ground up with sustainability and the planet’s best interests at heart.
Algorand relies on a pure Proof-of-Stake (PPoS) mechanism. This ensures that every token holder can participate in the block validation, eliminating the energy-intensive race seen in Proof-of-Work systems. The Pure PoS model gives us a network that’s not only decentralized and secure but also remarkably energy-efficient.
As we’ve come to expect from green crypto projects Algorand actively champions initiatives that align with its eco-friendly ethos. From supporting carbon offset programs to fostering collaborations that drive environmental conservation, Algorand is on the frontline of the green crypto revolution.
Key Points
- Consensus Mechanism: Pure Proof-of-Stake
- kWh per transaction: 0.0002 kWh
- Carbon Neutral: Yes
4. Cardano (ADA)

Founded by Charles Hoskinson, an Ethereum co-founder, Cardano is another top candidate to wear the green crypto crown. The key to Cardano’s success is its Ouroboros protocol, the world’s first peer-reviewed, verifiably secure blockchain consensus.
This Proof-of-Stake (PoS) mechanism ensures that energy consumption is minimal. Unlike a competitive cryptocurrency mining race, validators are chosen based on the amount of ADA they’ve staked in the network. This results in a drastic reduction in energy use without compromising security or decentralization. Some analysts have declared that Cardano is over 47,000x more energy efficient than Bitcoin.
But Cardano’s commitment to the environment goes beyond just its consensus mechanism. The network actively engages in research and partnerships to further sustainability in the blockchain sector. Cardano fans aren’t just in it for the tech; they’re in it for the planet.
Cardano’s blend of academic rigor, technological innovation, and environmental consciousness positions it as a frontrunner in the quest for a sustainable crypto future.
Key Points
- Consensus Mechanism: Ouroboros (Proof-of-Stake variant)
- kWh per transaction: 0.5479 kWh
- Carbon Neutral: Not currently, aims for Carbon negativity in the future
5. Stellar (XLM)
Coming in at number four, Stellar (XLM) leverages its unique consensus protocol known as the Stellar Consensus Protocol (SCP). Unlike the energy-intensive Proof-of-Work, this mechanism relies on a set of validators that come to an agreement without the need for exhaustive computational battles. A system that’s not only fast and scalable but also remarkably energy-efficient.
But Stellar’s eco-journey is more profound than just its consensus mechanism. The network has been vocal about its commitment to sustainability. By reducing the overall energy footprint and actively supporting eco-friendly initiatives, Stellar aims to redefine what it means to be an environmentally responsible digital asset.
Stellar’s partnerships with various financial institutions and payment gateways further its cause, ensuring that eco-friendly practices are not just limited to the blockchain but are also integrated into real-world financial solutions.
Key Points
- Consensus Mechanism: Stellar Consensus Protocol
- kWh per transaction: 0.00022 kWh
- Carbon Neutral: No, aiming to be Carbon neutral
6. Chia (XCH)

Chia emerges as a breath of fresh air in the bustling crypto marketplace, championing a novel approach to sustainability and redefining the essence of blockchain operations.
Unlike the traditional energy-guzzling blockchains that rely on computational battles, Chia introduces a groundbreaking consensus mechanism known as “proof of space and time.” This allows users to harness their unused hard drive space, eliminating the need for power-hungry hardware.
The network actively promotes using renewable energy sources for its farming operations. By encouraging its community to adopt green energy solutions, Chia aims to cultivate a truly sustainable and planet-friendly ecosystem.
Key Points
- Consensus Mechanism: Proof of Space, Proof of Time
- kWh per transaction: 0.023
- Carbon Neutral: No
7. XRP

Originally founded by Jed McCaleb and Arthur Britto, XRP is one of the OGs of the crypto space and one of Bitcoin’s first real competitors. Naturally, the developers poured their efforts into making XRP as energy-efficient as possible.
Despite its age, XRP remains one of the more eco-friendly cryptos in the industry. Thanks to its unique consensus mechanism, the XRP Ledger avoids the exhaustive energy costs enforced by Proof-of-Work chains.
On top of that, Ripple has also committed a $100M pledge to an environmentally sustainable future. This involves introducing future carbon offsetting initiatives that aim to make the protocol carbon-neutral by 2023.
Key Points
- Consensus Mechanism: Ripple Consensus Protocol
- Kwh per transaction: 0.0079
- Carbon Neutral: Not currently, but expecting carbon neutrality by 2030
Honorable Mention
While our focus has been on the champions of green crypto, Ethereum’s commitment to the cause is worth mentioning.
One of the giants of the crypto world, Ethereum has historically been associated with high energy consumption due to its old Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism. In September 2022, Ethereum performed a pivotal technological shift and successfully transitioned to a Proof-of-Stake network. This event was called ‘The Merge.’
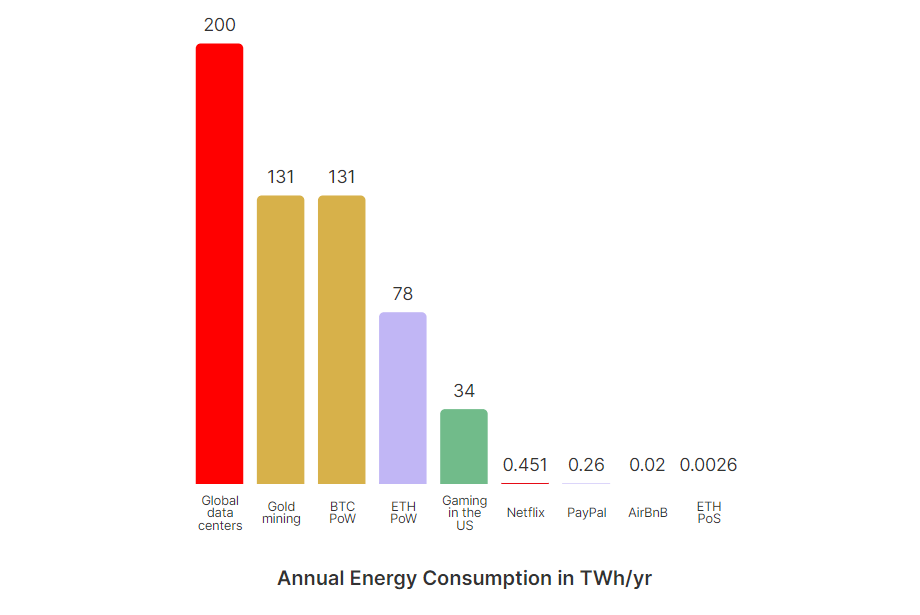
‘The Merge’ signifies Ethereum’s reincarnation as Ethereum 2.0, a more scalable, secure, and, importantly, energy-efficient network version. This monumental shift reduced Ethereum’s energy consumption by a staggering 99.95% in real-time, bringing it closer to other eco-friendly blockchains.
Do Blockchains Really Care About the Environment?
One of the biggest criticisms from crypto detractors is that all this talk of carbon offsetting and energy-efficient blockchains is just cherry-picked data and social media marketing ploy laden with virtue signaling.
Even if there is an element of truth behind these accusations, it doesn’t change the fact that making a conscious effort to reduce their energy consumption is a net positive for the industry and the planet.
While carbon offsetting doesn’t inherently make a certain kind of technology more eco-friendly, it shows that the company behind the product is aware of its environmental impact and is trying to mitigate any negative effects.
Pros and Cons of Green Cryptos
Green cryptos are emerging as an integral part of the blockchain industry, weaving an eco-friendly and innovative narrative. Let’s recap the pros and cons of eco-friendly blockchain projects.
Pros
- Good For The Planet seems obvious, but I’ll say it anyway. Green crypto projects are environmentally friendly, meaning they help protect and support the living ecosystem around us.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint – By design, green cryptos consume significantly less energy than older blockchains, reducing their carbon footprint.
- Financial Incentives – As the world shifts towards sustainable practices, green cryptos will receive more favorable regulatory treatments and potential tax incentives, making them attractive to sustainability-conscious investors.
- Wider Adoption – With their eco-friendly ethos, green cryptos can appeal to a wider audience, including environmentally conscious investors and institutions, paving the way for broader adoption.
- Innovative Technology – Green cryptos often come with cutting-edge consensus mechanisms and features, offering enhanced scalability, security, and transaction speeds.
- Combats Crypto Stigma – As more green crypto projects emerge, the old argument that cryptocurrency is bad for the environment will slowly dissolve.
Cons
- Emerging, Unproven Technology – As many green cryptos are relatively new, they might face technological challenges, bugs, or vulnerabilities that must be addressed over time.
- Market Volatility – Like all cryptocurrencies, green cryptos are subject to market volatility, which might discourage people from investing in emerging technology.
- Regulatory Uncertainties – The crypto landscape is ever-evolving, and regulatory stances can change. Green cryptos are not immune to potential regulatory challenges despite their environmental benefits.
On the Flipside
- While PoS consensus mechanisms are far more energy efficient than PoW models, some people would argue that it’s less secure and provides an imbalance of power to those with larger stakes in the network.
Why This Matters
In a world where ESG Investing is used to screen projects based on their Environmental, Social, and Governance policies, the importance of sustainability in the crypto space cannot be overlooked.
FAQs
While ‘The Merge’ reduced Ethereum energy consumption by over 99%, it’s still not the most energy-efficient crypto in the blockchain industry.
Yes, blockchains like Solana and Hedera have low rates of energy consumption and strong commitments to carbon neutrality or carbon negativity.
Compared with Bitcoin and other legacy blockchains, Cardano has far lower energy consumption rates and a smaller carbon footprint.
