
Like all blockchains in the cryptocurrency industry, Hedera Hashgraph promises fast, cheap transactions and unmatched security in DLT (Distributed Ledger Technology). It’s nothing we haven’t heard of before, but the Hedera network brings a unique twist to Web3.
It’s not technically a blockchain.
At face value, Hedera Hashgraph serves all the same purposes as traditional blockchains like Ethereum (ETH) or Cardano (ADA). You can store digital assets, use dApps and trade NFT collectibles. Despite the similarities, the Hedera Network is built differently under the hood.
Sponsored
What exactly is a hashgraph? How is it different from a blockchain, and why does it enable the Hedera Network to charge a flat transaction fee of just $0.0001?
What Is Hedera Hashgraph?
Hedera Hashgraph is a decentralized public ledger and cryptocurrency ecosystem. Unlike Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum, which are blockchains, the Hedera Network stores and transmits data on a directed acyclic graph.
Sponsored
For the end user, this doesn’t make much difference to how we experience the network. Hedera Hashgraph smart contracts are mostly written in Solidity, the same as Ethereum. Hedera Hashgraph is EVM-compatible, meaning if you are familiar with Ethereum, you’ll be right at home on Hedera.
How Does Hedera Hashgraph Work?
Hedera Hashgraph claims its unique hashgraph consensus algorithm is faster, safer, and more secure than traditional blockchain infrastructure. This is crucial for a public network, as it means that the Hedera network should be able to support thousands of users worldwide.
The Hashgraph – A Directed Acyclic Graph
The Hashgraph network is a type of directed acyclic graph. But how is a DAG different from a blockchain? Traditional blockchains form a line of interconnected blocks, or units of data. In a blockchain, network nodes or miners reach a consensus and validate new blocks using data from the previous block.
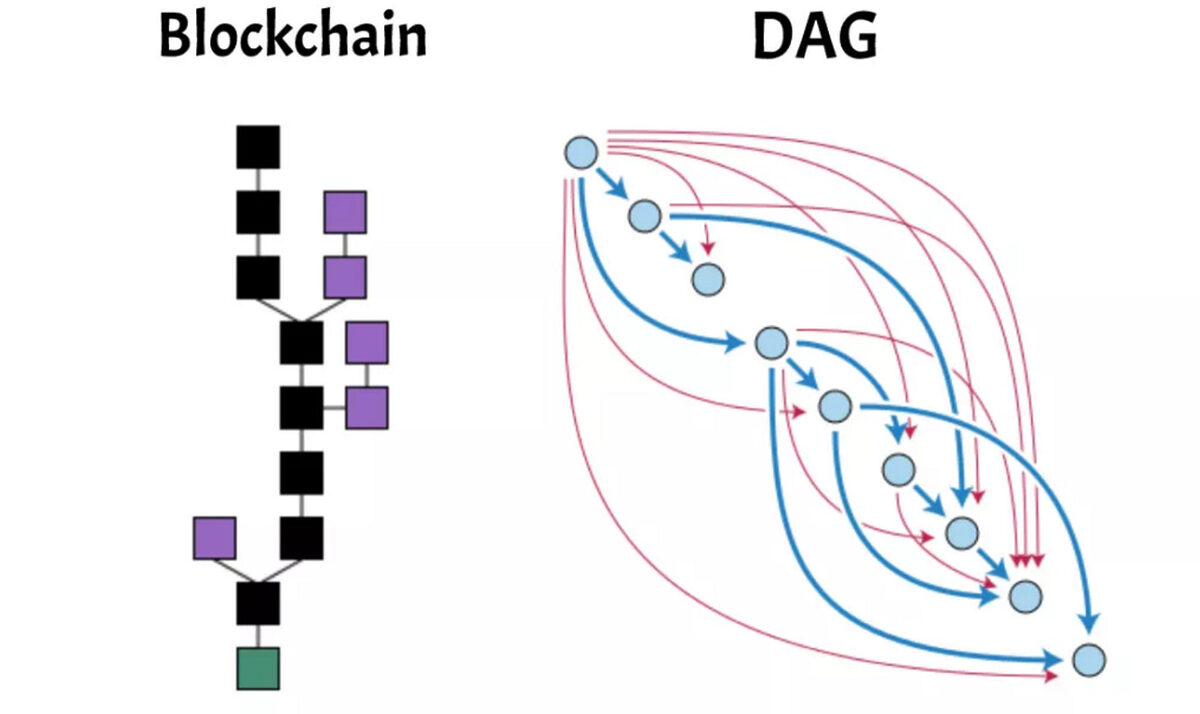
In a DAG, nodes can reference data from any block in the chain’s lifespan, allowing them to verify information and confirm transactions faster. This is one of the main reasons behind the Hedera Network’s high throughput of transactions.
The Hashgraph takes this one step further. It actively registers the timestamp of every transaction and digital signature in real-time, as well as the last hash sent and received by each node in the network. Hedera calls this phenomenon the gossip about gossip protocol, which helps put transactions in order on the network and ensures that all nodes are ‘telling the truth’ and reaching consensus.
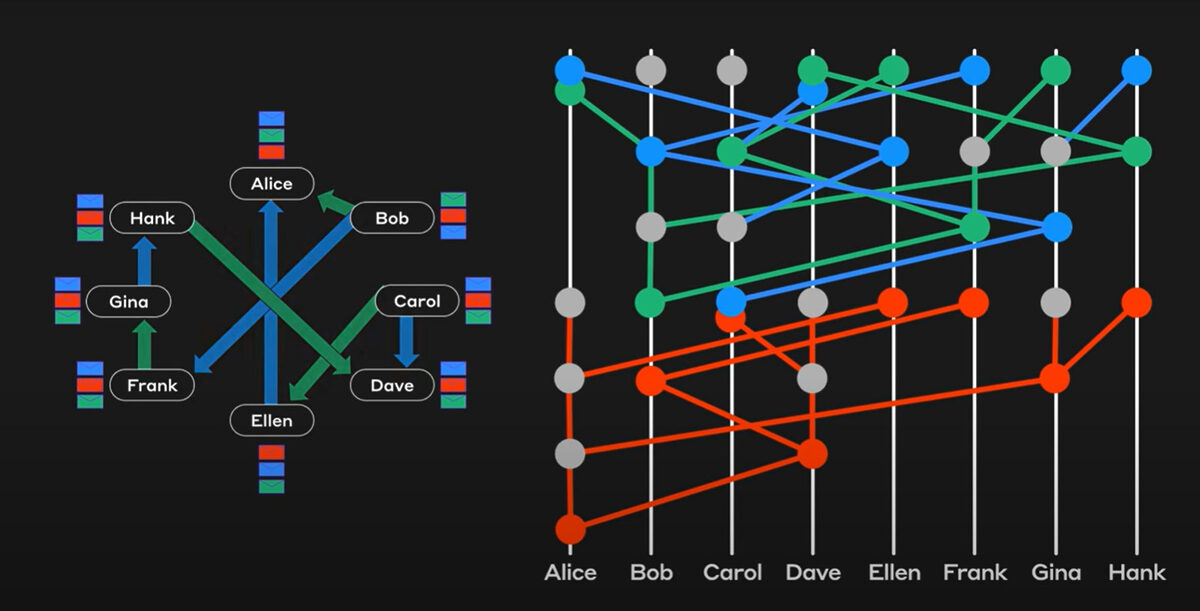
Source: Hedera Hashgraph
The gossip about gossip protocol is powered by a Proof-of-Stake mechanism. HBAR coins are staked to the network by node operators to secure the network and validate the hashgraph consensus.
Thanks to the hashgraph consensus, Hedera Network achieves asynchronous byzantine fault tolerance, or ABFT. This is a fancy crypto jargon term that means nodes agree with network transactions. ABFT isn’t foolproof because it only requires 66% of nodes to agree for a consensus to be reached. Anyone controlling over 34% of the network might be able to get away with malicious behavior.
HBAR – The Hedera Token

HBAR is the native cryptocurrency of the Hedera hashgraph network. The use cases for HBAR are similar to other Layer-1 altcoins. HBAR is required to pay transaction fees on the mainnet and secure the Hashgraph through the PoS consensus.
A Hedera crypto wallet and HBAR tokens let you explore the range of permissionless dApps, like decentralized exchanges on the hashgraph. HBAR is also the exchange currency in which Hedera non-fungible tokens, or NFTs, are priced.
It’s worth mentioning Hedera Hashgraph’s impressive network services and performance metrics. According to the team, the Hedera Network can process over 10,000 transactions per second. This significantly outperforms existing blockchain technologies like Ethereum, which struggle to clear 20 transactions per second.
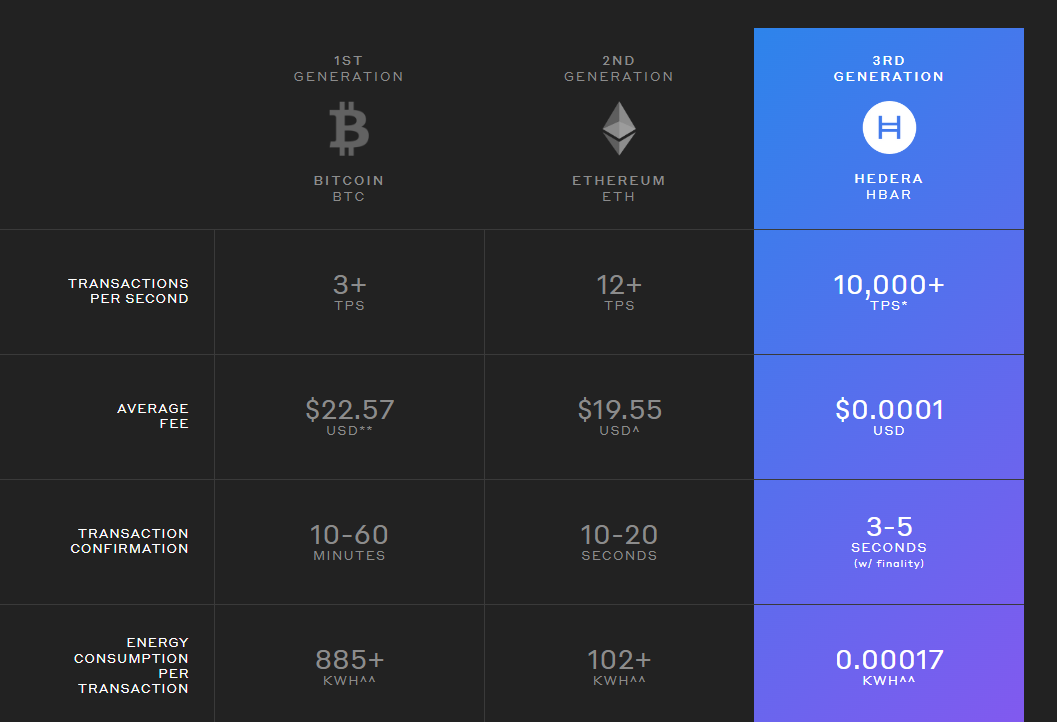
Source: Hedera Hashgraph
What’s more, the hashgraph enables the network to charge a flat fee of $0.0001 for network transactions, regardless of network congestion and HBAR price.
Hedera Governing Council
The Hedera Governing Council is an elite group of up to 39 international companies that oversee the growth and development of the Hedera Hashgraph ecosystem. The Council was formed to ensure the Hedera network would always enjoy decentralized governance and network stability and is made up of some of the world’s largest companies, including IBM, Google, and Boeing.

Source: Hedera Hashgraph
Is Hedera Hashgraph Truly Decentralized?
One of the Hedera Governing Council’s unique responsibilities is to decide who is and isn’t allowed to operate a validator node and secure the hashgraph. This raises some questions about whether or not Hedera Hashgraph is truly as decentralized as they promise to be.
In contrast, anyone with sufficient ETH can launch a node on the Ethereum network. Whether or not you’re allowed to operate a network node on Hedera Hashgraph is decided by a centralized source. This is expected to change as the Hedera network finds its feet in the cryptocurrency industry.
Moreover, when Hedera Hashgraph initially launched, its codebase was not open-source. This was done to prevent the chain from being forked but raised concerns about whether or not the Hedera Network was operating in the true spirit of decentralization. Developers needed a license from Hedera before building applications on the network.
Fortunately, the Hedera Governing Council followed through on their promise to make their infrastructure open source in 2022.
Hedera Hashgraph History & Founders
Hedera Hashgraph was launched by co-founders Leemon Baird and Mance Harmon in 2018. The Hashgraph itself is actually a product of Baird and Harmon’s software company Swirlds, which they founded together in 2015.
Swirlds is a key player in the Hedera Ecosystem. The company has patented the hashgraph software and is guaranteed a place on the Hedera Governing Council for the entire lifespan of the Hedera ecosystem.
Pros and Cons of Hedera Hashgraph
The ins and outs of directed acyclic graphs and asynchronous byzantine fault tolerance are dense and complicated. To bring things back to earth, let’s bypass the complex jargon and clarify the simple pros and cons of the Hedera Network.
Pros
- Fast – Hedera Hashgraph can process over 10,000 transactions per second, making it one of the most performant Layer-1 networks available
- Affordable – Every transaction on the Hedera network will cost the user less than a penny, regardless of network congestion and HBAR price
- Energy efficient – The Hedera Hashgraph network uses significantly less power than traditional blockchains and has implemented carbon offsetting initiatives to go fully carbon negative
- Sustained growth – There have been over 1.9 million accounts created on the Hedera mainnet, with more being added every day
- Accessible – The Hedera network is EVM-compatible, meaning its user experience will be familiar to anyone who’s used Ethereum before. What’s more, developers can easily port over Ethereum-based dApps to the Hedera network with minimal friction.
Cons
- Hedera is not as decentralized as it appears – The Hedera Governing Council still controls who is allowed to operate a node on the network. It could also be argued that Swirlds, the company that invented the hashgraph has greater control, power, and influence over the fate of network.
- Undeveloped ecosystem – Despite its position as a top 50 cryptocurrency in terms of market cap, few decentralized applications are built on the Hedera network. According to DeFiLlama there are only six DeFi apps on the network.
On the Flipside
- From a technical standpoint, Hedera Hashgraph is a fascinating network with excellent growth potential. However, it will struggle to attract users until it has a more developed ecosystem.
- The Hedera network is not the only cryptocurrency network that uses a directed acyclic graph. Other layer 1s like Fantom Opera also use this technology and have attracted far more users and developers.
Why You Should Care
The Web 3 world is expanding beyond simple blockchain systems. Projects like Hedera Hashgraph prove there are always creative new ways to improve network infrastructure and drive innovation in the crypto industry.
FAQs
Hedera Hashgraph is a network that uses distributed ledger technology to send and receive digital assets like HBAR and NFTs and host decentralized applications.
It is improbable that hashgraph will replace Bitcoin. While hashgraph is a powerful and creative technology in its own right, Bitcoin is a historic and iconic blockchain asset recognized worldwide.
Google is one of the companies that make up the Hedera Governing Council, a group that collectively owns and guides the future development of the Hedera Hashgraph Network.
If Hedera Hashgraph’s native cryptocurrency, HBAR, reached $1, it would have a market cap of 50 billion USD. That would make HBAR larger than BNB at current prices in April 2023.
According to CoinMarketCap, the all-time high price of HBAR is $0.57. This HBAR price was recorded on the 16th of September, 2021.
