
Decentralized exchanges are a staple of the on-chain crypto experience and one of decentralized finance’s first major use cases. DEXes have come a long way since Uniswap opened its first liquidity pools on the Ethereum (ETH) blockchain. Still, the lawless world of DeFi continues to confuse and discourage newcomers from dipping their toes in often-troubled waters.
With growing fears around crypto exchanges following the collapse of Sam Bankman Fried’s FTX disaster, self-custody and DeFi trading seem like a simple solution. For people looking to trade crypto assets without using centralized exchanges like Coinbase or Binance, a DEX provides everything they could need.
What exactly is a decentralized exchange, and how do they work? Why would I trade digital assets on a mysterious DEX instead of a trusted CEX?
Sponsored
Most importantly, are decentralized exchanges safe?
What Is a Decentralized Exchange?
A decentralized exchange is an application traders use to buy and sell cryptocurrency on-chain without relying on an intermediary or central authority to handle the transaction.
These decentralized platforms are popular with traders who don’t want to be exposed to counterparty risk or provide personal information to crypto exchanges through KYC (Know-Your-Customer) procedures.
Sponsored
They also offer an infinitely larger selection of tradeable tokens due to the permissionless nature of DeFi trading. While this sounds like a positive feature, it’s a double-edged sword. Because anyone can list tokens on a DEX, there are inevitably thousands of scams and fake tokens launched constantly.
How Do Decentralized Exchanges Work?
Decentralized exchanges are a profound and fascinating use case of blockchain technology where innovation and creativity run wild. A cornerstone of the DeFi ecosystem, DEXes use smart contracts to create a peer-to-peer marketplace where users trade tokens without giving custody of their assets to a central authority.
If I trade cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin (BTC) or Ethereum, on a centralized exchange, I rely on them to handle the transaction on my behalf. The trade occurs between off-chain accounts. These accounts, and any digital assets within them, are controlled by the exchange, not by me, the user.
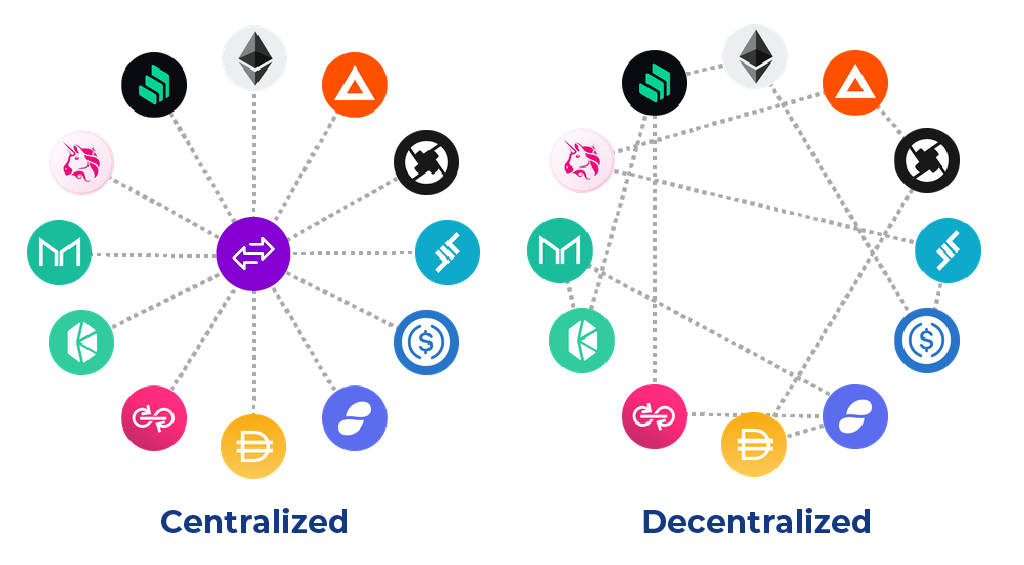
On a decentralized exchange, I trade directly with other users on-chain through dApps like Uniswap or Bancor using assets stored in my crypto wallet. I have full control of my cryptocurrency and don’t need to trust an intermediary to handle the transaction.
In the true spirit of decentralization, crypto trading on a DEX is inclusive and anonymous. It doesn’t require you to provide any personal information. Anyone with an internet connection and a crypto wallet can access these financial services.
Different Kinds of Decentralized Exchanges
While all decentralized exchanges more or less aim to serve the same purpose, they all have different algorithms and methods. The three most common types of decentralized exchanges are automated market makers, order books, and aggregators.
Automated Market Maker (AMM)
AMMs are the most common decentralized exchange type and are arguably the easiest to use. In an AMM, liquidity providers deposit their crypto tokens into trading pools, also called liquidity pools. These pools of tokens create a permissionless market that traders interact with to exchange tokens instantly.
Source: Uniswap
As a reward for providing their crypto assets into these trading pools, liquidity providers earn a small percentage of transaction fees from traders who use the pool. This encourages users to create trading pairs and earn crypto rewards.
Liquidity pools on popular AMMs like Uniswap and Sushiswap comprise just two tokens. However, some creative AMMs like Balancer let you deposit in pools with up to eight different cryptos. Other platforms like Curve Finance are specifically designed for stablecoin swaps.
Other examples of AMMs on alternative networks include PancakeSwap on the Binance Smart Chain and Trader Joe on the Avalanche blockchain.
Order Book
If you’re more comfortable with the interface of leading cryptocurrency exchanges like Binance but want to explore the world of crypto trading on-chain, an order book DEX is your best option.
Source: dydx
Using an order book DEX, traders enjoy all the features of professional exchanges, like setting specific limit orders and margin trading. The difference is that all buy and sell orders are registered on-chain, allowing for greater control over assets.
Like in an AMM, an order book DEX collects trading fees from users. In most cases, these fees are redistributed to DAO members who help to govern the platform. For example, by staking $GMX tokens, holders can earn rewards collected from the dApp’s trading volume.
A few examples of an order book DEX include GMX, Perpetual Protocol, and dydx.
DEX Aggregator
As the name would suggest, a DEX aggregator scours the blockchain to find the best price and lowest fees for any token swap imaginable. One of the biggest issues in DeFi is the lack of liquidity compared to centralized exchanges.
Source: Kyber Swap
DEX aggregators help traders find the most efficient swap rates and avoid high slippage costs in decentralized finance. Popular examples of DEX aggregators include 1inch and Kyber Swap.
Why Use a DEX to Trade Cryptocurrency?
There are plenty of great reasons to trade crypto on a decentralized exchange. DeFi holds great opportunity for savvy traders, but with high reward comes high risk.
What are the benefits and drawbacks of trading on a decentralized exchange?
Pros
- Find hidden gems – When trading on a DEX, you can find emerging crypto projects before they get listed on mainstream centralized exchanges. For example, SHIB traded on decentralized exchanges long before it became a top 20 cryptocurrency.
- It’s accessible and anonymous – If privacy is an issue, trading on a DEX means swapping your favorite tokens without providing personal information to a centralized exchange. Moreover, anyone can trade on a DEX from anywhere in the world. All you need is a crypto wallet.
- Open Source contracts – Most DEXes, like Uniswap, are open-source projects. This means anyone can read, verify and audit their code and smart contracts to ensure they’re safe to use and free of vulnerabilities.
Cons
- Low liquidity – As a rule of thumb, decentralized exchanges simply cannot match top crypto exchanges’ deep liquidity and trading volume. It’s different for large-scale traders to move large sums without causing disruptive price volatility or excessive slippage.
- Unvetted pairs – Anyone can create and list tokens on a decentralized exchange. While this brings limitless opportunity, it also means thousands of scam tokens are out there trying to catch unwary buyers and steal their funds.
- Hacks – Even though security firms audit most DEXes, hackers can still find malicious new ways to hack a protocol’s code and steal funds. If a hacker is able to get hold of your private keys, they’ll also be able to take control of some functions in your wallet and access your funds.
On the Flipside
- Decentralized exchanges are the first novel use case of decentralized finance and are actively building upon the foundations of Bitcoin and the cryptocurrency movement. That said, plenty of growing pains still limit their effectiveness and discourage users.
Why You Should Care
As crypto expands and evolves, decentralized exchanges will only become more efficient, secure, and frictionless. They’re a cornerstone of the DeFi movement, and knowing how to use them properly can benefit any crypto enthusiast.
FAQs
Using daily trading volume as the reference metric, Uniswap is the largest decentralized exchange in the crypto industry. It is closely followed by dydx, a decentralized order book exchange.
No, decentralized exchanges are perfectly legal in most of the world. However, in countries where crypto is banned, some laws may be against their use.
No, Binance is managed and operated by a central authority. The company has full control over the platform and all the assets stored on it. This makes Binance a centralized exchange.
Popular decentralized exchanges include Uniswap, Pancakeswap, dydx, Curve Finance, and Balancer.
