
Solana smart contracts are a fundamental part of the network’s ecosystem. Designed with scalability in mind, these high-performance programs are used throughout on-chain dApps and projects throughout the Solana ecosystem, including your favorite DeFi and NFT protocols.
But smart contracts are hardly a revolutionary feature in the cryptocurrency market, with dozens of Layer One blockchains all providing this service. Yet, Solana has emerged as one of the leading platforms for blockchain development.
Sponsored
This begs the question: What about the Solana network makes it such a popular development environment?
Table of Contents
What Are Solana Smart Contracts?
Solana smart contracts are programs written and stored on the Solana blockchain that automatically runs whenever certain conditions are met. They power on-chain activities like token swaps and automatic transfers.
Because smart contracts are executed automatically, they provide an efficient means of eliminating intermediaries and ensuring that the terms of an agreement between two parties are honored.
Of course, smart contracts are not exclusive to Solana. Most Layer One blockchain networks, including Ethereum (ETH) and Cardano (ADA), support smart contract development.
Sponsored
Yet, Solana smart contracts are arguably more efficient than its rivals, thanks to the blockchain platform’s greater speeds and lower transaction fees. Solana’s unique hybrid consensus mechanism combines Proof-of-Stake (PoS) and Proof-of-History (PoH) models to ensure maximum efficiency.
What Are Solana Smart Contracts Used For?
Now that we better understand what Solana smart contracts are, let’s consider some of the typical use cases.

The most popular and common use of smart contracts on the Solana network is seen in DeFi. Decentralized finance is a movement that aims to give everyone on earth unhindered access to financial services while maintaining their privacy.
DeFi applications like decentralized exchanges and lending markets are commonplace on Solana, making managing your digital assets on-chain easier than ever. This also extends to the network’s thriving NFT scene, with collectors trading their favorite pieces using smart contracts.
But that’s just scratching the surface. Solana smart contracts power dozens of crypto gaming projects on the network. They are also responsible for handling the blockchain’s growing number of DePin and RWA platforms. For example, Parcl is a creative application that enables users to trade indexed Real Estate markets across the globe.
Essentially, smart contracts can streamline and simplify any process that involves confirming agreements between several parties. For this reason, blockchain technology is expected to revolutionize dozens of industries worldwide, including supply chain and logistics, healthcare, and education.
Practical Information about Solana Smart Contract Development
If you’re a newcomer to the ecosystem or you’re bridging over from rival chains, there are a few basic things you’ll need to know.
First of all, Solana’s main programming language is Rust. While Ethereum and most other EVM-compatible networks rely predominantly on Solidity, the Rust programming language is believed to be better designed to operate at scale and compile quickly and efficiently.
Before developing Solana smart contracts, developers must familiarise themselves with the wider Solana development environment. This includes downloading essential developer tools like the Solana CLI (command line interface), Solana SDK (Software Development Kit), and relevant frameworks like Anchor.
If any of these terms are confusing or fill you with dread, never fear! We’ve included a brief glossary at the bottom of this page, simplifying some of the denser topics.
It is also highly recommended that you use the Solana devnet during the development process. This sandbox environment lets you test smart contract code, APIs, and all associated program logic before deploying directly on the Solana mainnet.
Is the Solana Blockchain Popular among Developers?
As one of the top Layer One blockchains in the crypto industry, it’s unsurprising that Solana enjoys high levels of developer activity.
In aid of this, Solana Labs has provided comprehensive documentation that helps budding developers hit the ground running. Additionally, the Solana Foundation proposes generous grants and funding to provide emerging startups with the resources they need to turn innovative ideas into practical realities.
The evidence is somewhat inconsistent if we look closely at developer activity on-chain. For example, Artemis data suggests that Solana enjoys more total repositories than all other chains, bar Ethereum but fewer weekly commits than Ethereum Layer 2s.
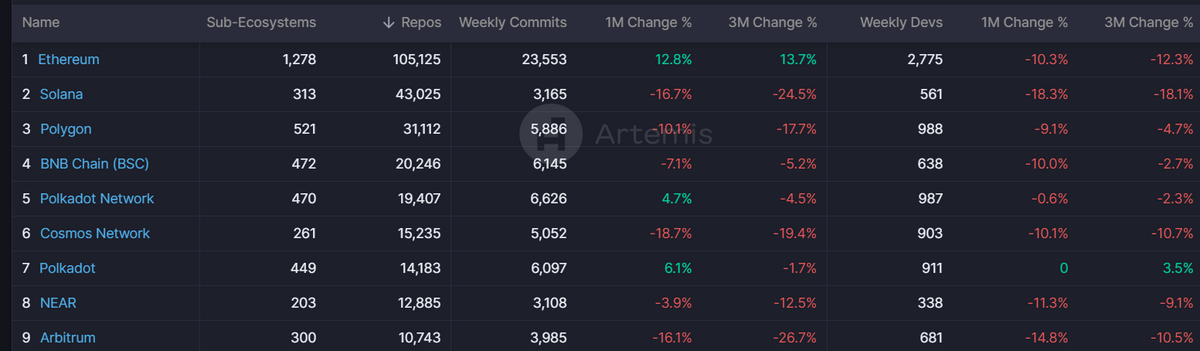
Likewise, Electric Capital’s developer report shows that Solana has more developers than rivals like Avalanche and Cardano but is still well behind top EVM chains like Polygon and Arbitrum.
Why Solana?
While Solana still has plenty of work to catch up to kingpin Ethereum, the network still provides an excellent environment, making it popular amongst users and developers.
Solana’s high speeds, impressive throughput, and low gas fees primarily mean that it’s perfectly positioned to support mass adoption. The network is completely open-source and, despite struggling initially, has improved its levels of decentralization and security.
The number of validator nodes on the network continues to climb, while exciting developments like the Firedancer validator client promise to push Solana’s scalability to even greater heights.
Glossary of Key Terms
Blockchain technology is not for the faint of heart. Complex terminology is often used casually, making it hard for beginners to understand exactly what’s been discussed.
- Consensus Mechanism – The algorithm and model by which blockchains confirm that transactions are valid and secure. The mechanism also creates new blocks.
- Smart Contract – A self-executing program that automatically runs when certain conditions are met.
- Command Line Interface – A CLI is a text-based environment that runs programs, manages files, and interacts directly with your computer.
- Transaction Throughput – Generally measured in transactions per second, transaction throughput is the most common method of measuring blockchain speed and scalability.
- Compiler – A compiler is a tool that translates human-readable source code into machine code that is read by the computer.
- Programming Language – In the same way humans use languages like English, French, and Japanese, software developers write code in different programming languages. Different languages offer different utilities and have distinct advantages and disadvantages.
- Software Development Kit – An SDK is a prescribed set of tools used to create and manage software for a particular platform.
On the Flipside
- Solana smart contracts are not terribly unique in themselves and generally offer similar utilities to what you find on other Layer 1 blockchains like Ethereum or Cardano.
Why This Matters
Solana is one of the most popular and performant blockchains in the crypto industry. Understanding the use cases and limitations of its infrastructure and use cases will help you make informed decisions in the crypto market.
FAQs
The Solana network supported smart contract functionality when it launched in March 2020.
No, smart contracts on the Solana blockchain are predominantly written in Rust.
As the original Layer One blockchain, Ethereum boasts more smart contracts than any other network.
