
DePin, or Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks, are being touted as the next big thing. On top of having a long and over-complicated name, crypto influencers across the space are promising that DePins will revolutionize the industry and bring fresh, new utilities to cryptocurrency and blockchain technology.
But hang on a second. Wasn’t that also the case for DeFi, DeSo, and the Metaverse? DePin projects claim to be the bridge between blockchain and the real world, but haven’t we heard all this before?
What are DePins, and are they truly everything they’re cracked up to be?
Table of Contents
What are Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks?
DePins, also known as decentralized physical infrastructure networks, are applications and protocols that aim to provide services in the real world. Unlike other crypto movements, like DeFi and NFT technology, DePins use blockchain technology to streamline how ordinary people live their everyday lives.
Sponsored
For example, NATIX is an emerging DePin project that operates the world’s largest decentralized camera network. NATIX users are incentivized to submit video data in return for crypto rewards, or in-app points.
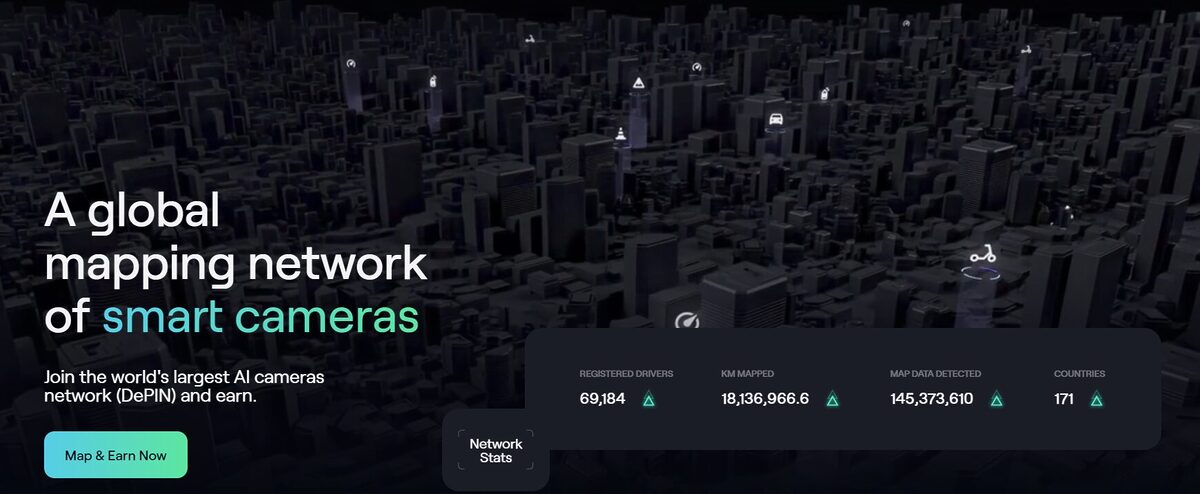
We’re surrounded by hundreds of cameras daily, from CCTV cameras to the smartphone in your pocket. Yet, less than 10% of this video footage is analyzed, which leaves huge amounts of high-quality data unused.
Sponsored
By analyzing this previously wasted data, smart cities can vastly improve our quality of life. Sectors like crime prevention and traffic congestion will have far greater access to video data and theoretically help us live safer and smoother lives in the cities of the future.
Another way to think of DePins is to imagine infrastructure services like telecommunications, transport, and energy. However, instead of these services being provided by private companies, they’re powered by decentralized communities of users and token holders.
How Do DePins Work?
DePins are, at heart, decentralized and community-driven service providers. They provide a way for emerging startups to quickly raise capital and deploy hardware and infrastructure by sharing governance and revenue with a community of supporters.
Let’s imagine the step-by-step creation and deployment of the Web3 DePin project that runs renewable energy grids:
- Infrastructure Proposal – An enterprise envisions a public service, like renewable energy grids, and prepares to launch its business.
- Crowdsource Funds – With a vision in mind, the project begins raising funds by selling hardware, like solar panels, and governance/rewards cryptocurrency tokens to investors.
- Protocol launch – At this stage, solar panels have been widely distributed across the world to various investors. This also helps decentralize the project and ensure it’s not vulnerable to a single point of failure. The project officially launches, and solar panel operators can sell generated energy to buyers through on-chain smart contracts.
- Growth – As the project grows, solar panel operators earn crypto incentives as a reward for using the platform and providing renewable energy to buyers. In a perfect world, the value of these tokens also increases because they provide governance power and earning potential from within the project itself.
- Improve Service Offerings – If the project is successful and the provided services continue to accrue value, the project can dedicate more resources to expanding the infrastructure and hardware. This will, in turn, increase token rewards for service providers and the value of the native digital asset.
Essentially, DePin networks provide a new way for emerging startups to rapidly raise capital and get their business off the ground while giving investors and supporters greater control over their rewards and involvement in the project.
By building these projects on decentralized networks, providers, consumers, and end users can bypass middlemen and intermediaries while transacting data, services, and materials in a transparent and secure way.
DePin Use Cases
Now that we’ve better understood what DePins are and how they work let’s consider what kind of services and platforms can be built using this technology.
So far, the leading projects in the DePin sector are focused mainly on decentralized data storage and cloud computing platforms.

Crypto projects like Filecoin (FIL) aim to provide a decentralized, cost-effective alternative to Amazon Web Services, while Render (RNDR) offers GPU-based rendering solutions and allows node operators to monetize their unused computational power.
Looking to the future, we’re seeing decentralized infrastructure projects tackle everything from electric car battery charging, satellite telecommunications, noise pollution data tracking, and even decentralized mapping through platforms like HiveMapper.
Are DePin Networks a New Thing?
The DePin ecosystem seems to be the hot new thing in the crypto space, but it only takes five minutes of research to see that the concept has been around for years. Emerging dApps and protocols have always targeted physical world industries and use cases, so why all the fuss now?
As it would appear, DePin is a unifying term that covers a wide range of sectors. Historically, physical infrastructure protocols were divided into many niches, from IoT (Internet of Things) to supply chain logistics being categorized differently.
Fortunately, Messari, one of the leading research groups in the industry, put the matter to bed once and for all by hosting a poll. In a competitive race, DePin won out over alternatives like PoPW (Proof of Physical Work), TIIPN (Token Incentivized Physical Networks) and EdgeFi.
DePin Concerns
DePin platforms open plenty of doors for advancements within the crypto industry, but they’re far from foolproof. Plenty of obstacles still need to be considered before DePin projects are truly ready for mass adoption.
Blockchain networks need to be sufficiently scalable to support a growing user base. If the blockchain can’t handle the workload, there’s no point in onboarding millions of network participants to a DePin application.
Moreover, DePin projects are no more immune to failure than regular business models. Yes, providing a decentralized telecommunications network that rewards bandwidth providers with cryptocurrency is a nice idea, but if the project can’t attract end users to buy the product or service, it will still fail, with investors and supporters bearing the brunt of the losses.
DePin Pros and Cons
Decentralized physical infrastructure networks have plenty to offer but still have many hurdles to overcome. Let’s recap the pros and cons of DePins.
Pros
- Distributed Ownership – DePins allow people to diversify their income streams by providing infrastructure services to the public.
- Growth Potential – DePins make it easier for emerging businesses to crowdfund their products and get the ball rolling faster.
- Innovative New Use Cases – DePins brings a huge variety of novel use cases to blockchain technology and expands the capabilities of the industry.
Cons
- Limited by Chain Functionality – DePin projects can be launched on any smart contract capable chain, like Ethereum (ETH), Solana (SOL) or NEAR (NEAR). That being said, these chains need to be sufficiently scalable to handle the workload of thousands of users.
- Leadership Struggles – Decentralization is one of the key principles of the industry, but it can also be a flawed concept. The majority isn’t always right, and having decentralized governance doesn’t always mean the community will act in the project’s best interests.
On the Flipside
- DePins might be the shiny new thing in the market, but they’ve actually been around for a while now, albeit under a variety of different names.
Why This Matters
Learning about what DePins are and how they work will help you better understand the capabilities of these projects.
FAQs
DePin, or Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks, are applications and platforms that provide tangible services in the real world. Through token incentives, investors and supporters can earn income and govern the growth of the protocol.
DePin applications are possible on all smart contract-compatible networks, like Ethereum, Solana, and Cardano.
