
Bitcoin maxis, beware! The Stacks crypto project is here to extend the Bitcoin blockchain beyond its limitations, bringing improved functionality to the world’s largest cryptocurrency network.
One of the biggest concerns about Bitcoin (BTC) is its lack of utility outside of being a self-custodial digital asset payment network. The Stacks blockchain liberates Bitcoin from these limitations, building DeFi apps and NFTs on top of Bitcoin’s impenetrable security.
What is Stacks (STX)? How does this innovative Bitcoin layer work behind the scenes? Is it truly a threat to other smart contract-capable networks like Ethereum (ETH) and Cardano (ADA)?
What Is Stacks (STX)?
Stacks is a Layer-1 blockchain capable of supporting smart contracts. It aims to unlock the full potential of Bitcoin by providing an ecosystem of dApps and products that are settled on the world’s most secure and decentralized blockchain.
Sponsored
Not only does the Stacks network bring greater utility to Bitcoin, but it also seeks to resolve its scalability issues with higher transaction throughput. Could Stacks be the ultimate solution to Vitalik Buterin’s symbolic blockchain trilemma?
Why Does Bitcoin Need Stacks?
Despite Bitcoin’s position as the world’s top cryptocurrency, it’s often criticized as being nothing more than a decentralized store of value. As a payment network, many alternative blockchains like XRP are faster and more affordable.
Sponsored
On top of that, the Bitcoin blockchain doesn’t support smart contracts, making it infinitely less useful than a network like Ethereum that hosts a multitude of DeFi apps. Apart from sending and receiving BTC between wallets, there’s not much you can do with Bitcoin.
As a digital asset, BTC represents over $500 billion of liquidity but offers no way to leverage this value creatively. For example, there are no decentralized exchanges or lending platforms on Bitcoin.
Stacks solves this problem and brings integral blockchain functions, like decentralized finance and NFT technology, to the Bitcoin network.
How Does Stacks Work?
The Stacks network is an execution layer that settles complex transactions using the Bitcoin blockchain as a base layer.
At the core of this process are two unique features of the Stacks protocol. These are the Proof-of-Transfer (PoX) consensus algorithm and the Clarity programming language.
Proof-of-Transfer (PoX)
The Proof-of-Transfer consensus mechanism is the key link between Stacks and Bitcoin. It’s an extension of the Proof-of-Burn algorithm, wherein miners burn crypto as a proxy in exchange for computing resources to secure the chain.
Instead of burning tokens in exchange for computing resources, tokens are committed to the Stacks protocol and transferred between network participants. We call these Miners and Stackers.
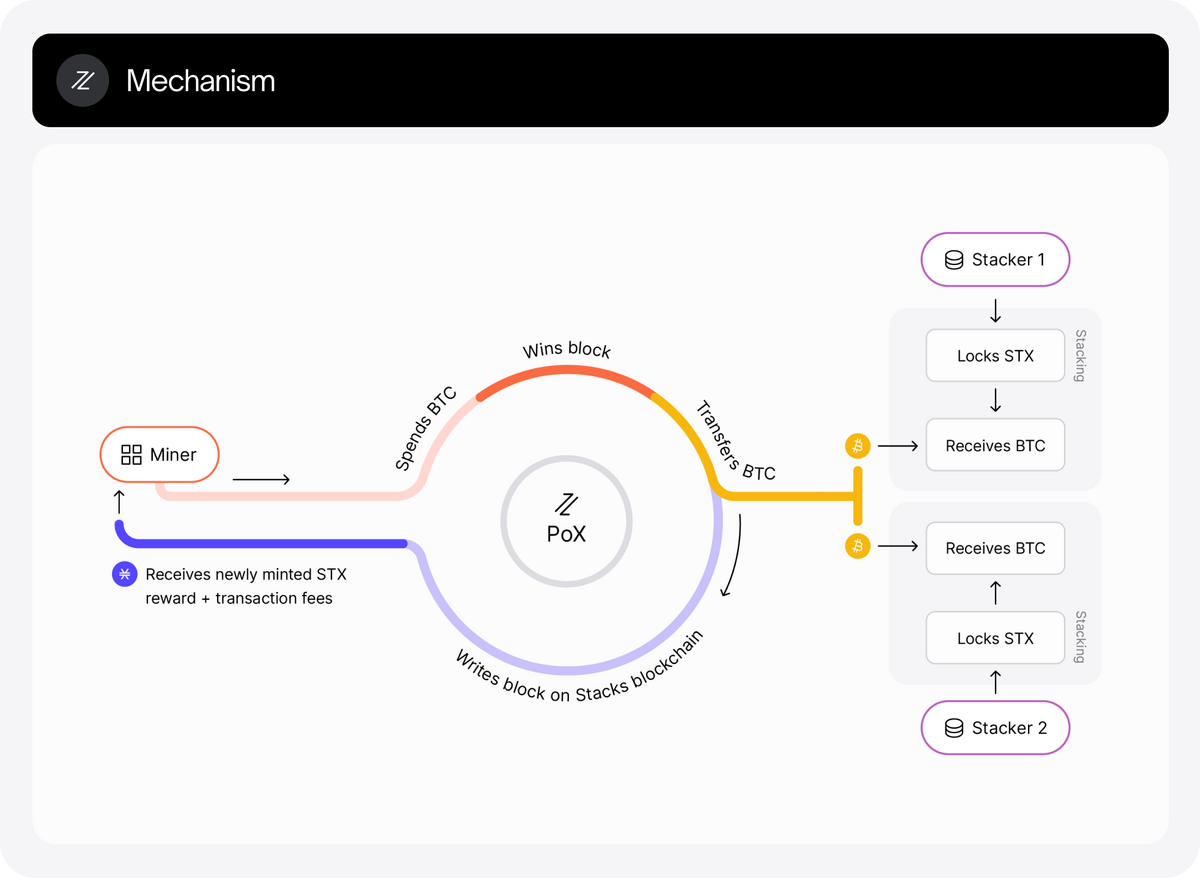
Source: Stacks
Miners transfer BTC to Stackers, hoping to win block rewards and transaction fees from the Stacks network. The chances of winning the block correspond to the amount of BTC committed.
On the hand, Stackers lock their STX tokens to the network in exchange for BTC committed to the network by Miners. After their lock-up period is complete, Stackers reclaim their STX tokens.
Clarity
Clarity is a smart contract programming language unique to the Stacks network. It’s optimized for predictability and security and was specifically designed to combat common exploits seen in Solidity, Ethereum’s dominant language.
Here are some of the key features of the Clarity programming language:
- Uncompiled – Clarity contracts are committed to the network exactly as they are written. In many other languages, contracts are compiled into byte-code before being submitted to the chain. This leaves room for the contract’s missing aspects in translation, potentially opening the door to vulnerabilities.
- Decidability – When writing Clarity contracts, developers can guarantee that program execution will terminate after a finite number of steps. This also makes it easier to ascertain transaction costs, meaning you’ll never need to worry about running out of gas halfway through a transaction.
- Bitcoin compatible – Clarity smart contracts are designed to read the state of the native Bitcoin blockchain. This means developers implement Bitcoin transactions directly into their applications for seamless smart contract triggers.
The STX Token
STX is the native cryptocurrency of the Stacks blockchain. The Stacks token is used to pay transaction fees on the network and can be ‘stacked’ to earn BTC through the Proof-of-Exchange consensus mechanism. It’s also used in the network’s various dApps as collateral and a currency of exchange.
Interestingly enough, Stacks STX emissions replicate Bitcoin’s halving cycle. Stacks block rewards are synchronized with Bitcoin halvings and cut in half roughly every four years.
Stacks History
Originally named Blockstack, the company was founded in 2013 by Ryan Shea and Muneeb Ali with the vision of solving pain points in web applications. Coming out of Princeton University, the startup was approved through the Y Combinator accelerator in 2014.
In 2019, Blockstack became the first company ever to receive approval from the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission to sell digital assets. The SEC-regulated token offering raised over $23 million.
Following a full rebrand to Stacks in October 2020, the company published a new white paper outlining its plans for Stacks 2.0, the Bitcoin-adjacent execution layer we use today.
The Stacks Ecosystem
The Stacks ecosystem is home to a range of decentralized applications, wallet software, and NFT collections. While the Stacks network is still relatively young, the Stacks Foundation offers plenty of grants and funds incentivizing developers to join the ecosystem.
Stacks DeFi
Decentralized exchanges and lending platforms are typically the cornerstone DeFi apps on emerging blockchains. Apps like StackSwap, Alex, and Zest Protocol are basic DeFi providers within the Stacks network.
Source: StackSwap
The Arkadiko Protocol creates the leading stablecoin, USDA, on Stacks. Like Tether (USDT), USDA is pegged to the value of the U.S. Dollar.
Stacks NFTs
Bitcoin NFTs continue to gain traction in the Web3 world. While Ordinals have been the main driving force behind Bitcoin NFTs, the Stacks NFT ecosystem has been witnessing its own renaissance.
Gamma.io has established itself as the leading NFT marketplace for Bitcoin Ordinals and Stacks NFTs. Megapont Ape Club is the most well-known NFT collection on the Stacks network, generating over five million STX in trading volume.
Stacks Wallets
Hiro Wallet is undoubtedly the most widely used and trusted Stacks Wallet. With over 280,000 downloads, it tracks the value of your account in real-time and is the best place to store Ordinals and Stacks NFTs.
Users can also participate in the Proof-of-Exchange consensus and ‘stack’ STX coins to earn BTC rewards. The Hiro Wallet is available as both a desktop app and a browser extension.
Stacks Pros and Cons
Now that we have a better understanding of the Stacks protocol and how it works, let’s briefly recap its benefits and drawbacks.
Pros
- Scalable – The Stacks network addresses one of Bitcoin’s biggest faults: scalability. By breaking down blocks into micro blocks, Stacks can reach high transaction throughput and significantly reduce transaction fees when compared to the native Bitcoin blockchain.
- Access Bitcoin Liquidity – BTC is the largest source of liquidity in the crypto market, but its lack of utility is a massive obstacle to adoption. Stacks resolves this issue and brings greater functionality to the world’s largest cryptocurrency.
- Secure Native Programming Language – Clarity is designed to solve the pitfalls and common exploits of other smart contract languages. While this doesn’t guarantee that every contract on Stacks is watertight, it leaves less room for error and offers increased user security.
Cons
- Low user count – Despite the innovation on display and the creativity of the PoX consensus, the Stacks network has struggled to attract high user numbers and TVL (total value locked). According to DefiLlama, the Stacks network has amassed less TVL than other small networks like Hedera Hashgraph, despite targeting the biggest source of liquidity in the space.
- Small ecosystem – The range of applications available within the Stacks ecosystem pales compared to other blockchains. Coins with similar market caps, like Fantom, have almost ten times the number of dApps while similarly valued to STX.
On the Flipside
- The issues facing the Stacks network are, at face value, easily solvable. Generous incentive programs and grants are already in place to kickstart the growth and development of the blockchain.
Why You Should Care
Bitcoin is the face of the cryptocurrency industry, and its lack of utility is a poor reflection of the incredible progress being made in other realms of blockchain technology. By bringing new utility to BTC, the Stacks network is a net positive for the entire blockchain industry.
FAQs
The STX token has a max supply of 1,818,000,000 and a circulating supply of roughly 1,300,000,000.
You can buy Stacks STX tokens on leading crypto exchanges like Binance or Coinbase, or through the official Hiro Wallet.
In the crypto market, the only certain thing is volatility. Just because a project has interesting technology doesn’t mean it’s automatically going to be a good investment. You should always conduct your own thorough research before investing in any cryptocurrency.
BlockStack was originally founded by Ryan Shea and Mubeen Ali in 2013. The project was rebranded to Stacks in 2020.
According to CoinMarket, STX price reached its all-time high of $3.61 on November 16, 2021.
