
The Cardano vs. Polkadot debate is one of cryptocurrency’s fiercest and most polarizing matchups. Born from the profound and mysterious minds of Ethereum’s (ETH) co-founders, these decentralized ecosystems provide modern solutions to the key problems faced by legacy blockchains.
Having comfortably established themselves as some of the largest cryptocurrencies in the industry, these blockchain networks are often pitted against each other. However, what many crypto asset enthusiasts don’t realize is that Cardano and Polkadot are actually very different.
Sponsored
In this guide, we’ll weigh up the functions and capabilities of these heavyweight blockchain platforms and see how they compare head-to-head.
Table of Contents
Cardano vs. PolkaDot: Blockchain Basics
Before diving into a comparison of these third-generation blockchains, it’s crucial that we first clarify a basic understanding of what these ecosystems aim to achieve and how they work.
What Is Cardano (ADA)?

Amongst crypto purists, Cardano is popularly considered the utopian blockchain network. Meticulously designed by academics and boasting peer-reviewed network architecture, Cardano is a research-driven blockchain ecosystem.
Charles Hoskinson, one of the original Ethereum co-founders, launched Cardano in 2017 after disagreements with fellow ETH team members. The Layer One network aims to address the scalability, sustainability, and interoperability issues that plague legacy blockchains like Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum.
Sponsored
Today, Cardano boasts a thriving ecosystem complete with a wide variety of dApps across DeFi, Cardano NFTs, and other products and services in the cryptocurrency market.
The team’s sustained commitment to improvement has meant that new Cardano upgrades and hard forks are constantly being rolled out to make the mainnet even more powerful.
Strengths
- Research-Driven – Cardano is the first blockchain platform to be built through peer-reviewed research, ensuring a robust and fault-tolerant system.
- Two-Layered Architecture – Cardano boasts a unique two-layered structure, separating the settlement layer from the computational layer, and allowing for greater flexibility and security in smart contract execution.
- Sustainability – With its Ouroboros consensus mechanism, Cardano offers a more energy-efficient alternative to Proof-of-Work systems.
- Scalability – Cardano’s novel Layer-2 Scaling solution, Hydra, is expected to bring transaction higher throughput and transaction speeds to the network. Tie this in with the Cardano blockchain’s low transaction fees and you have a recipe for success.
What Is Polkadot (DOT)?

Polkadot is a multi-chain interchange and translation architecture, this kind of blockchain network is often called a Layer-0 network because it allows other blockchains to be built on top of its foundations.
Envisioned by Gavin Wood, another co-founder of Ethereum and the creator of the Solidity programming language, Polkadot launched in 2020. Instead of providing a direct competitor to Ethereum, Polkadot aims to facilitate easier communication and interoperability between networks.
Think of Polkadot as an interconnected network of independent blockchains that can all transfer data and communicate with each other. Polkadot’s main chain is called the Relay Chain, which acts as a hub for each individual blockchain, or Parachain.
Strengths
- Interoperability – Polkadot’s enable’s different blockchains to communicate and share information, breaking down the barriers that previously existed between individual blockchain ecosystems.
- Parachains – These are individual blockchains that run in parallel within the Polkadot ecosystem, allowing for diverse applications and use cases to be developed.
- Adaptive Scalability – Polkadot’s architecture is designed to scale organically as more valid transactions are added to the network, ensuring that the system can handle future demands.
- Sustainability – Polkadot uses a variation of the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm, making it decentralized and energy-efficient.
Key Differences Between Cardano and Polkadot
The first thing you’ve probably noticed is that, despite their similarities, Cardano and Polkadot are fundamentally different. While Cardano provides a decentralized network for dApp development and smart contracts, Polkadot aims to provide greater interoperability to networks that choose to build upon its foundations.
Despite their differences, both Cardano and Polkadot share the common goal of advancing the Web3 world. Let’s explore how the unique approaches and core philosophies that make these networks special.
Development Philosophy
Cardano’s development is characterized by its rigorous academic and scientific approach. Every protocol upgrade and feature is peer-reviewed by experts, ensuring a solid and secure system.
The Polkadot network, on the other hand, emphasizes practicality and adaptability. It’s designed as a “Layer-0” blockchain that connects various “Layer-1” blockchains, acting as a foundation upon which other projects can build and interoperate.
Architecture
Cardano’s two-layered architecture distinctly separates the settlement layer, where transactions occur, from the computational layer, where smart contracts are executed. For the end user, this means that Cardano hosts a growing range of dApps and tools directly on its network.
Polkadot’s architecture revolves around its Relay Chain, which connects various parachains (individual blockchains) and helps them communicate. This means that the applications built on Polkadot’s individual parachains enjoy greater interoperability than you might find on other networks.
Consensus Mechanism
Cardano employs the Ouroboros Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism, which is energy-efficient and offers water-tight security against malicious actors and cyber attacks.
Polkadot uses the Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS) mechanism, which allows for a set of validators to be elected by the network’s stakeholders to secure the relay chain.
Ultimately, the two algorithms are similar and achieve the same goals. Stakers contribute their ADA or DOT tokens to nominated pools to secure the network and validate new blocks. Both are well-decentralized and energy-efficient.
Tokenomics
ADA is the lifeblood of the Cardano blockchain. The native token has a capped supply and is used for paying transaction fees and securing the network.
Likewise, DOT is the native crypto asset of the Polkadot network. While it has the same utilities, namely paying transaction fees and ensuring the stability and security of the network, DOT has an inflationary supply, with new tokens being minted to reward DOT stakers.
Environmental Impact
Blockchain technology has long been criticized for its disastrous effects on the environment. While Bitcoin uses as much electrical energy as a small nation and has a carbon footprint that leaves much to be desired, modern blockchains are breaking the stereotype.
Cardano and Polkadot, as well as the crypto market’s other emerging altcoins like Solana, are celebrated for their efforts around sustainability. For example, one Solana transaction uses less energy than a Google search.
A study by CCRI explored the energy consumption of top Proof-of-Stake crypto networks. The findings were remarkably profound, but for the sake of brevity let’s take a look a the overall results.
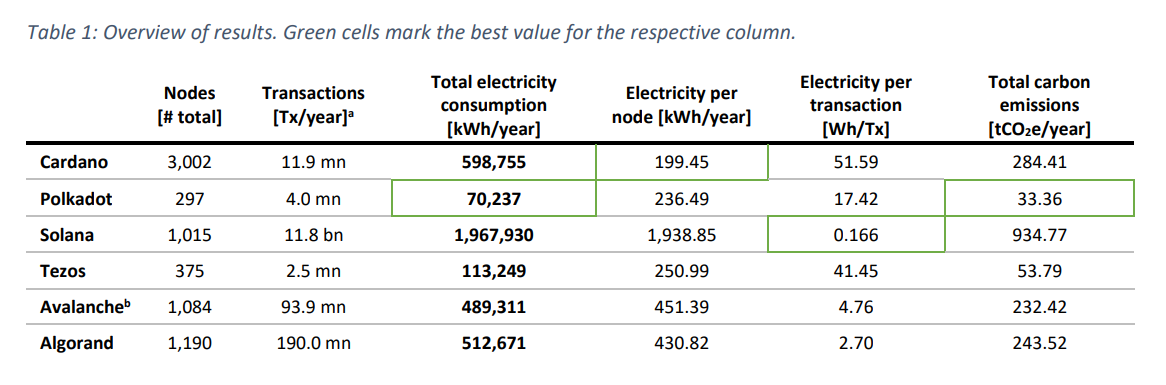
CCRI found that of all the networks studied, Polkadot had a far lower total energy consumption based on kWh/year. While this sounds great for Polkadot, don’t be deceived. Gavin Wood’s network has far fewer users than Cardano’s, meaning it requires less power.
If we change our approach and check the average electricity consumption per node, Cardano edges out Polkadot. Charles Hoskinson’s network is the cream of the crop, with each node averaging around 199.45 kWh/year.
Cardano vs. Polkadot: Head to Head
Another way to look at the Cardano vs. Polkadot debate is to break both networks down into quick key facts that recap the network’s basic features and capabilities.
| Metric | Cardano (ADA) | Polkadot (DOT) |
| Founder | Charles Hoskinson | Gavin Wood |
| Launched | 2017 | 2020 |
| Transactions Per Second (TPS) | 250 | 1000 |
| Market Cap | $9.1B USD | $4.9B USD |
| Max Supply | 45,000,000,000 ADA | N/A |
| Inflationary | No | Yes |
| All-Time High | $3.10 (Currently down -91.58%) | $55 (Currently down -92.66%) |
Final Verdict
All things considered, comparing Polkadot and Cardano is like comparing apples and oranges and deciding which would make a better beef steak. Despite certain similarities in the founding teams and basic architecture of the blockchains themselves, Cardano and Polkadot serve different functions in the crypto market.
It boils down to this: Cardano is a Layer One blockchain with its own ecosystem of dApps, tools, and services. On the other hand, Polkadot is a foundational network that blockchains like Cardano can build on top of and communicate with other networks in the Polkadot ecosystem.
Alone, Cardano is larger than Polkadot and arguably has a better chance of succeeding long-term based on its higher usage rates and wealth of platforms.
However, if a couple of Polkadot’s parachains like Moonbeam or Astar are able to attract more users and build dynamic and unique ecosystems in their own right, there’s no reason why Polkadot couldn’t eclipse Cardano’s position in the market.
Disclaimer: You should always do your own research and never take any subjective opinions at face value. Take everything you read online with a grain of salt and ignore sensationalized price predictions.
On the Flipside
- Cardano and Polkadot were both blockchain platforms that punctuated the previous crypto market bull run in 2021. As the years wear on, these platforms may be replaced by newer blockchains that are built on more advanced technology.
Why This Matters
Cardano and Polkadot are two of the largest and most popular cryptocurrencies in the blockchain industry. Learning what they are and how they work will help you to make informed decisions in the space.
FAQs
Comparing Cardano and Polkadot is difficult because the two blockchain platforms serve different purposes. Cardano is a Layer-One blockchain, while Polkadot is a foundational ‘blockchain-of-blockchains’.
Hypothetically, Cardano could replace Ethereum. However, given Ethereum’s established dominance and network effect, it is unlikely.
Kusama is Polkadot’s canary network. This means that Kusama provides an experimental development environment for projects that intend to build on Polkadot in the future.
