
Bitcoin’s Lightning Network is gaining serious traction as the leading solution to BTC’s scalability concerns. With industry heavyweights like Binance setting up Lightning Nodes and nations like El Salvador rolling out support for the scaling solution, the Bitcoin Lightning Network is primed for mass adoption.
New Bitcoin Lightning Wallets and channels are being created daily, demonstrating the demand for instant payments and low transaction fees.
In this guide, we’ll look into the Layer-2 network designed to improve upon Satoshi Nakamoto’s iconic crypto asset and explore how it works. Can this Bitcoin (BTC) scaling solution take on Web2 leaders like Visa? Or are Lightning Payments just a flash in the pan?
Table of Contents
What Is the Bitcoin Lightning Network?
The Bitcoin Lightning Network is a “Layer-2” payment protocol that operates on top of Bitcoin’s blockchain. Think of it like a high-speed expressway that runs parallel to the main network that processes fast and affordable payments.

Despite being a technical revolution in its own right, the Bitcoin network is ill-suited for mass adoption. Unlike modern blockchains, Bitcoin transactions are painfully slow and often charge high transaction fees.
Bitcoin’s Lightning Network aims to maintain the crypto asset’s status as a store of value, like digital gold, while creating a scalable and secure payment system that rivals existing platforms.
How is this possible?
How Does the Lightning Network Work?
The mechanics of the Lightning Network are as fascinating as they are innovative. Imagine a bustling network of tunnels, each connecting two individuals who wish to transact with each other. These tunnels, or ‘payment channels,’ are the core of the Lightning Network.
Sponsored
When two people decide to transfer BTC using the Lightning Network, they establish a payment channel that runs parallel to the Bitcoin blockchain. Imagine this channel as a private highway allowing them to exchange unlimited transactions without congesting the main blockchain.
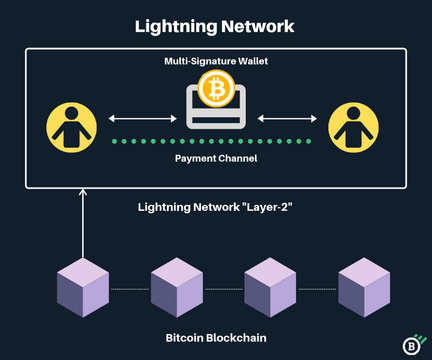
These off-chain transactions are not immediately broadcasted to the Bitcoin network. Instead, they are held within the channel, away from the prying eyes of the public ledger.
When the channel is closed, The final balance of transactions is settled as a single transaction on the Bitcoin blockchain. Like Ethereum (ETH) Rollups, this method allows large groups of transactions to occur off-chain, with only the opening and closing of the channel being recorded on-chain.
On top of that, the Lightning Network has an ace up its sleeve. Thanks to smart contract technology, it doesn’t require a direct channel between all users. For example, if Vitalik has a channel with CZ, and CZ has a channel with SBF, Vitalik can transact with SBF through CZ, creating a network of interconnected channels.
If you want to set up a Lightning Wallet and transfer digital assets, don’t miss our helpful step-by-step guide on Lightning Payments.
Why Do We Need the Bitcoin Lightning Network?
As the popularity of Bitcoin soars, so does the strain on its network. The Bitcoin blockchain, while revolutionary, was not designed to handle a high volume of transactions simultaneously. The rise of Ordinal NFTs and BRC-20 tokens has proven this, with Bitcoin gas fees exploding to all-time highs in 2023.
This limitation led to slower transaction times and higher fees, making Bitcoin payments a poor way of exchanging funds. Think of it this way; you won’t use BTC to pay for a coffee if the transaction fee costs more than the coffee itself!
The Bitcoin Lightning Network is designed to address these very challenges. By moving transactions off the main blockchain, the Lightning Network significantly increases Bitcoin’s scalability, enabling it to handle millions of transactions per second. This starkly contrasts the Bitcoin network’s capacity, which can handle fewer than ten transactions per second.
Moreover, the Lightning Network drastically reduces transaction costs, making micropayments possible and economically viable. This opens up many new use cases, from tipping content creators fractions of a cent to paying per article read or video watched.
Lightning Network History
The concept of the Lightning Network was first introduced in a white paper by Joseph Poon and Thaddeus Dryja in 2015. They envisioned a second-layer solution that could solve the scalability issues plaguing Bitcoin.
Since then, the development of the Lightning Network has been a collaborative effort, with several teams working on different protocol implementations. These include Blockstream, Lightning Labs, and ACINQ, each contributing to the evolution of Bitcoin’s most popular scaling solution.
The first successful transaction on the Lightning Network took place in 2017, marking a significant milestone in its development. Since then, the network has grown exponentially, with thousands of active nodes and channels.
What’s Next for Lightning Network?
The future of the Lightning Network looks bright. While the network is still in its early stages, there’s a flurry of ongoing development to enhance its capabilities and user experience. These include toolkits that help developers build DeFi applications and NFT functionality within the Lightning Ecosystem.
One of the key areas of focus is improving the network’s routing capabilities to ensure transactions find the most efficient path across the network. As the network grows, seamless channel routing will be crucial for maintaining the speed and low cost of transactions.
There’s also a growing interest in integrating the Lightning Network with other cryptocurrencies. This could enable instant, low-cost transactions across blockchains, further expanding the network’s utility.
The Lightning Network is also expected to play a significant role in developing decentralized applications (dApps). Its ability to handle micropayments efficiently could pave the way for new types of dApps, from pay-per-use services to decentralized streaming platforms.
Bitcoin Lightning Network Alternatives
While the Lightning Network aims to resolve Bitcoin’s scalability problems, it’s not the first payment system to threaten Bitcoin’s crown.
Alternative decentralized payment networks like Ripple (XRP) and Bitcoin forks like Litecoin (LTC) and Bitcoin Cash (BCH) also provide fast and affordable solutions. However, the key difference between these platforms is that the Lightning Network still takes advantage of Bitcoin’s unmatched security and decentralization.
If that wasn’t enough, BTC is considered a ‘safe haven’ by cryptocurrency standards. BTC’s price is far less volatile than its competitors, making it a more stable network for frequent transactions.
Pros and Cons of Bitcoin Lightning Network
As we delve deeper into the Bitcoin Lightning Network, it’s crucial to weigh the advantages and potential drawbacks of this innovative Layer-2 solution. Like any technology, the Lightning Network has its pros and cons that shape its utility and adoption.
Pros
- Fast – As the name suggests, The Lightning Network offers lightning-fast transactions. Payments are processed in milliseconds to seconds, significantly improving over the ten-minute block time of the Bitcoin network.
- Scalable – With the capacity to handle millions to billions of transactions per second, the Lightning Network outperforms the Bitcoin network’s transaction capacity.
- Low Fees – The Lightning Network enjoys low fees by executing transactions off-chain.
Cons
- Liquidity Constraints – Payment channels require upfront funding, which can tie up funds that could otherwise be used elsewhere.
- Counterparty risk – Technical issues or malicious actions from other users could result in funds getting stuck in a channel.
- Node centralization – There are concerns that the network could become centralized over time, as larger nodes with more channels and liquidity could dominate the network.
On the Flipside
- The Bitcoin Lightning Network is just one of the many payment networks in the crypto space. While it’s faster and more affordable than the main blockchain, it still relies on the Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism, which has been criticized for its high energy consumption.
Why This Matters
The Lightning Network solves one of Bitcoin’s biggest obstacles and makes the network a viable contender for a global payment system.
FAQs
Yes, Binance has begun accepting BTC deposits and withdrawals via the Lightning Network.
A Bitcoin Lightning Network Channel is like an off-chain tunnel connecting two network users. These users can send BTC to each other quickly without congestion the main blockchain.
No, you cannot buy Lightning Bitcoin. The Bitcoin Lightning Network uses the same crypto asset as the main blockchain, BTC.
