
Web4?! What on earth is Web4? Weren’t we just on the cusp of Web3 adoption? People are finally warming to the idea of Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), and blockchain technology. Yet, some theorists in the cryptocurrency industry have already fixed their gaze on the next shiny horizon.
The internet moves fast. Decentralized technologies and the crypto industry move even faster, so it makes sense that ‘the next generation of the internet’ is already being speculated about.
Web4 AI and Brain-Computer Interfaces promise to change how we use the internet forever, but what does that actually mean?
Sponsored
Being skeptical by nature, I’ve dived into the limited literature on Web4 to sort fact from fiction so that you don’t have to. In this article, we’ll explore the previous generations of the internet and take an objective look at the emerging technologies of Web4.
Table of Contents
The Evolution of the Internet
The internet has evolved dramatically since its inception, from a simple, static network of chunky, hyperlinked web pages to a dynamic, interactive, and increasingly decentralized platform.
Distinct phases have marked this evolution, each bringing its own set of innovations and challenges.
Web1: A Read-Only Internet
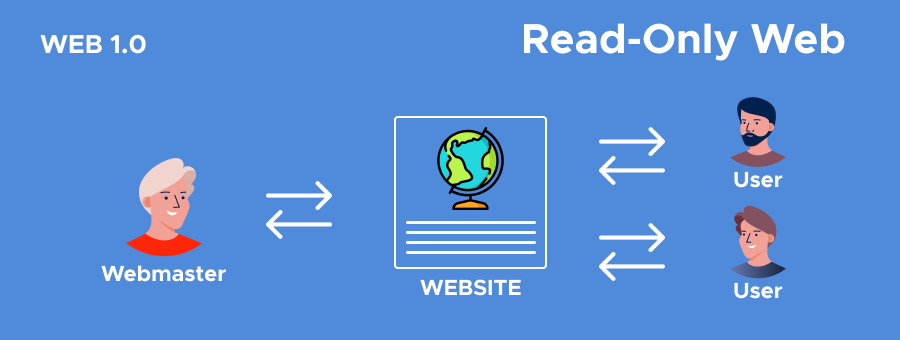
It seems strange to call it Web 1.0 now, but the original World Wide Web was exactly that. Also known as the “read-only web,” it was the first iteration of the Internet. Invented by Tim Berners-Lee, it was a static network of hyperlinked web pages where users could only consume information.
Sponsored
The lack of interactive elements and user control was due to the technological limitations of the time, including the absence of read/write functionalities and cloud systems.
Early detractors laughed at the idea of the World Wide Web. On an American talk show in 1995, David Letterman teased Bill Gates, ‘What about this Internet thing?’ and made jokes implying that existing inventions like radio and tape recorders made it redundant.
Web2: A Read/Write Internet

Web 2.0 marked a significant shift in the internet’s evolution, transforming it into a dynamic, interactive platform. It’s the most cherished and beloved internet we are familiar with today.
The advent of cloud computing characterized this era, improved read/write capabilities, content creation, and the explosion of social media platforms. Everyone, not just computer ‘nerds’, could now contribute to and expand the internet, creating content and sharing their ideas.
If Web 1.0 was like a book that people could read, Web 2.0 was more like a book with blank pages that people could fill. Web2 brought everything from blogs and community forums to online shopping, mobile apps, and remote startups.
Web2 gave birth to thousands of new use cases and business models, like online advertising. But the parabolic growth of Web 2.0 was something of a double-edged sword. It raised concerns about data privacy and ownership, as users’ personal data was often controlled by centralized entities, like Meta and Twitter.
Web3: A Read/Write/Own Internet

This brings us to where we are now, the Web3 revolution. Also called the semantic web, cryptocurrency enthusiasts consider Web3 an improved internet where new technologies like blockchain, cryptocurrency, and NFTs give users greater control over their assets, data, and identity online.
Decentralization is the key driving force of the Web3 movement. Instead of vast portions of the internet being controlled and owned by centralized entities and exploitative intermediaries, ownership is distributed among everyday users like you and me.
Through blockchain technology, cryptocurrency, and smart contracts, Web3 gave birth to decentralized finance (DeFi). DeFi is a central pillar of the Web3 world, giving everyone on the planet permissionless, trustless access to financial tools and services they were previously excluded from.
Internet users are no longer required to share their data with centralized entities or use them to transfer funds over the Internet. Instead, peer-to-peer networks, like Bitcoin and Ripple (XRP), give people full control and self-custody of their assets.
Where do we go from here?
Web4: The Symbiotic Web
Web 4.0 is the proposed next phase of the internet’s evolution. It’s envisioned as a more connected, intelligent, and personalized version of the Internet that draws on emerging technology like artificial intelligence.
Often referred to as ‘The Symbiotic Web’, Web4 promises to intertwine our lives and the internet more deeply than ever before.
What exactly does that mean?
What Is Web4?

Before diving into what we can expect from Web4, I need to clarify: Web4 is a purely theoretical concept that is fuelled entirely by speculation. The roadmap for what Web4 looks like is unclear, with theorists sparking off radical ideas.
Web4’s proponents present the next evolutionary stage of the internet as a decentralized web that fully incorporates new technologies to deliver an unprecedented internet user experience.
Artificial Intelligence
Web4 AI is expected to play a significant role in the next generation of the internet, enabling more dynamic and adaptable machine learning ecosystems that can learn from data and improve over time.
Like a giant universal ChatGPT, Web4 AI could lead to more personalized and efficient online experiences.
Brain-Computer Interfaces
If you thought Apple’s new VR/AR headset was impressive, Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI) is the next step up. BCIs allow humans to interact with computers using their thoughts by measuring brain activity and translating it into commands that computers can understand.
While undoubtedly a fascinating piece of technology, it all sounds rather dystopic. Just because we might be able to connect our brains to the Internet directly doesn’t mean we should. Even on top of all the ethical questions it raises, BCI connections seem like a massive security and health risk waiting to happen.
Metaverse

As we know, the Metaverse is a virtual reality space where users can engage in immersive experiences and interact with a vast array of digital content. If you ever saw Spielberg’s 2018 film ‘Ready Player One,’ you probably have a pretty good idea of what the Metaverse looks like.
Web4 seeks to expand the Metaverse, offering new avenues for social interaction, entertainment, and economic opportunities through blockchain-powered virtual assets.
Sound familiar? That’s because it is. All these features are already possible in the Web 3 world. This brings me nicely to my next point.
Is Web4 Really Any Different from Web3?
Apart from Brain-Computer Interfaces, everything Web4 theorists speculate about already exists within the Web3 world. Web3 aims to create a decentralized internet of permissionless, trustless applications, giving users self-custody and complete control over their digital assets.
Based on the information circulating the internet, Web4 has the same goals. One of the leading proponents of Web4, Anndy Lian, argues that “Web4 is more decentralized than Web3.”
He supports this claim, asserting:
“Web4 also aims to create decentralized applications (dApps) that run on decentralized infrastructure, which eliminates the need for intermediaries and centralized organizations to control and manage the applications.”
Maybe I’ve missed something, but replace Web4 with Web3, and you have the same sentence and the same idea.
At the same time, maybe I’m behaving just like David Letterman in 1995. It’s absolutely possible that while Web3 laid the foundation for decentralized applications and user ownership of data, Web4 will take it a step further by integrating advanced technologies to enhance the user experience.
Perhaps Web4 envisions a future where the boundaries between physical and digital realities blur, offering unprecedented possibilities that we cannot yet fathom.
Web4 Pros and Cons
Like any technological advancement, Web4 has its own advantages and challenges. Let’s objectively recap Web4’s pros and cons.
Pros
- Enhanced user experiences – Web4 promises immersive and personalized experiences, leveraging AI and the Metaverse to create dynamic and interactive digital environments.
- Improved efficiency – AI-powered automation in Web 4.0 could boost productivity, speed up time to market, and lower costs, giving businesses a competitive edge and better customer service.
- Expanded possibilities for cryptocurrencies – Web4’s advancements offer new opportunities for cryptocurrency integration, fostering innovation in areas like DeFi.
Cons
- Scalability – As the number of devices and people connected to the internet grows, it will become increasingly challenging to keep up with the demand.
- Security – As Web4 incorporates advanced technologies, ensuring personal data privacy and cybersecurity becomes more challenging, demanding robust security measures.
- Ethical implications – AI and BCIs raise important ethical questions regarding privacy, consent, and the potential misuse of personal information. Responsible development and regulation are vital.
On the Flipside
- While discussions turn towards Web4 and whatever that might mean for the future of the internet, Twitter creator and Bitcoin Maxi Jack Dorsey is already one step ahead. Dorsey is crafting Web5, an even more decentralized internet built on the Bitcoin blockchain.
Why This Matters
People are always looking for the next big thing in the crypto market. Web3 is well-established. We know what it is, and have tangible applications and use cases that we can take advantage of daily.
On the other hand, Web4 still asks more questions than it answers. It’s still unclear what Web4 will actually look like and how it differs from Web3.
FAQs
Web4 is the proposed next generation of the internet, which promises an improved user experience through emerging technologies like artificial intelligence.
At this point Web4 is purely speculative, with no concrete examples of its applications or use cases.
If you believe in cryptocurrency, decentralization, and the right self-custody of assets, then Web3 definitely has a future for you.
Parts of the Web3 world use crypto to transfer funds on peer-to-peer networks. However, the scope of Web3 is much larger than crypto alone and includes ownership and control of your data online.
