
- Bitcoin has been poised for a halving shakeup for about seven days, marking the first halving event since May 11, 2020.
- This pre-programmed change to miner rewards has promised to disrupt supply and demand.
- Past halvings have correlated with price surges; can lightning strike the same spot four times?
The cryptocurrency world is abuzz with anticipation as BTC approaches its next Bitcoin halving event, which is expected in just seven days. This pre-programmed occurrence within Bitcoin’s code promises to shake things up, but what exactly is a halving, and why does it generate such debate among crypto enthusiasts about its impact on the price of Bitcoin?
Table of Contents
Understanding Bitcoin Mining
Before we delve into what a halving is, it’s important to understand the concept of Bitcoin mining. Bitcoin mining is the process of creating new bitcoins and verifying transactions on the blockchain network.
Miners use specialized computers to solve complex mathematical puzzles. The first miner to solve the puzzle for a particular block of transactions earns the right to add that block to the blockchain, the public ledger that records all Bitcoin transactions.
Sponsored
As a reward for their work, miners are awarded a certain amount of Bitcoin. Mining plays a crucial role in the Bitcoin network. It not only creates new coins but also helps to secure the network.
Miners are competing to solve these puzzles, and the difficulty of these puzzles is constantly adjusted to ensure that new Bitcoin blocks are added to the blockchain at a consistent rate. This competition helps to ensure that the Bitcoin network is secure and tamper-proof.
Now that we understand Bitcoin mining and its importance, let’s explore Bitcoin halving and why it’s such a significant event.
What is a Bitcoin Halving?
A Bitcoin halving is a pre-programmed event written into Bitcoin’s code that cuts the mining reward for new blocks in half. This mechanism is designed to control the issuance of new Bitcoin and combat inflation over time.
Sponsored
Imagine miners as the security guards and record keepers of the Bitcoin network. It uses specialized computers to solve complex cryptographic puzzles, verify transactions, and add new blocks to the blockchain, a public ledger that records all Bitcoin transactions. In exchange for their efforts, miners are rewarded with a certain amount of Bitcoin for each block they successfully mine.
The halving reduces this reward by 50%, meaning miners receive less Bitcoin for their work. This incentivizes them to become more efficient in maintaining profitability and keeping the Bitcoin network secure. This reward system is crucial for the network’s operation but can’t last forever. That’s where the halving comes in.
Bitcoin halvings are programmed to occur roughly every four years or after every 210,000 blocks are mined. This effectively reduces the rate at which new Bitcoin enters circulation. With a finite supply of 21 million Bitcoins coded into the system, the halving ensures that all Bitcoins will be mined by around 2140.
Why Does the Halving Happen?
This seemingly simple change serves two critical purposes. Firstly, it controls the total supply of Bitcoin. Bitcoin’s design limits its creation to a maximum of 21 million Bitcoins. The halving mechanism gradually reduces the rate of new bitcoins entering circulation, mimicking gold’s finite nature and combating inflation.
This scarcity is a core principle behind Bitcoin’s value proposition. Imagine a rare gemstone, for example. The fact that only a limited number of these gemstones exist helps to drive up their value. Bitcoin operates on a similar principle.
The halving mechanism helps ensure that Bitcoin remains scarce and valuable over time by limiting the total supply and periodically reducing the rate at which new coins are created.
Secondly, the halving maintains network security. Miners dedicate immense computing power to secure the Bitcoin network, and the block reward incentivizes this participation. By periodically reducing the reward, the halving ensures that mining remains profitable enough to attract and retain miners, safeguarding the network’s robustness.
Without sufficient miners, the Bitcoin network would be vulnerable to attack. Halving helps mitigate this risk by ensuring that mining remains a financially viable activity. The halving acts like a safety valve for the Bitcoin network.
It ensures that new coins are introduced at a predictable rate, preventing inflation and maintaining the scarcity that underpins Bitcoin’s value. It also ensures the network remains secure by keeping mining profitable and attracting miners to participate in the verification process.
Looking Back: Past Performance of Previous Halvings
The last halving occurred on May 11, 2020, with the block reward dropping from 12.5 BTC to 6.25 BTC. The event was highly anticipated, leading to significant price volatility in the surrounding period. Proponents of the halving theory point to historical data suggesting price increases following previous halvings.
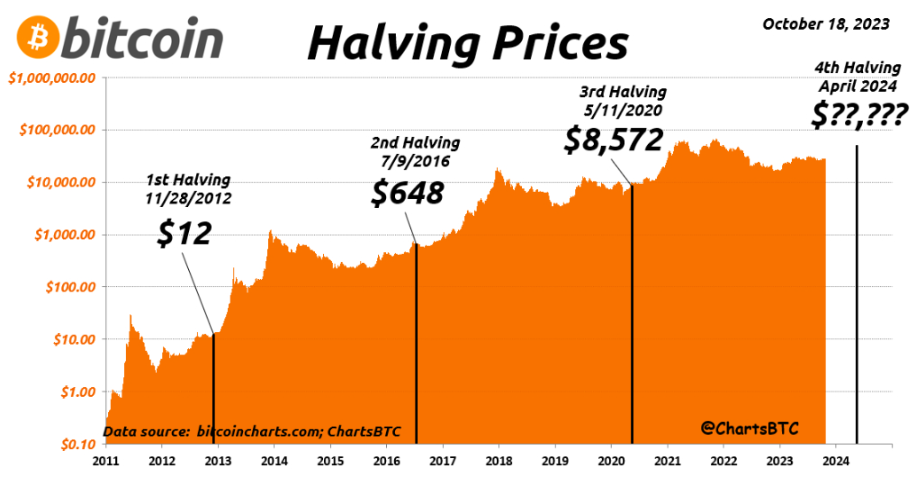
For example, after each of the 2012, 2016, and 2020 halvings, the Bitcoin price rose substantially from its halving day price to its cycle top. However, it’s important to remember that correlation doesn’t equal causation. Many other factors can influence Bitcoin’s price, and attributing price movements solely to the halving can be misleading.
Some argue that the significant price increases following previous halvings may not be repeatable. As Bitcoin matures and becomes more widely adopted, the halving’s impact on price may become less dramatic.
Why the Excitement?
With fewer new bitcoins entering circulation, existing bitcoins become relatively scarcer. This theoretical scarcity could drive up the price due to increased demand.
Imagine a treasure chest filled with gold coins. If you remove half the coins suddenly, the remaining coins will become individually more valuable, right? Bitcoin operates under a similar principle. By reducing the inflow of new coins, the halving creates a scenario where the existing bitcoins become more scarce in relation to the overall demand.
Think of it like a classic economic principle: supply and demand. If the supply of a good (Bitcoin) goes down, but the demand stays the same or even increases, the price of that good (Bitcoin) would theoretically rise. This is the core idea behind the belief that the halving can lead to a price increase for Bitcoin.
Additionally, proponents of the “halving theory” point to historical data suggesting price increases following previous halving events. This adds another layer of intrigue. While past performance doesn’t always indicate future results, historical trends can influence investor sentiment.
If investors see a pattern of price increases following halvings, they might be more likely to buy Bitcoin in anticipation of a similar rise this time around. This increased buying pressure could further contribute to a price increase.
Is a Price Surge Guaranteed?
The truth is, a surge in Bitcoin’s price following the halving isn’t guaranteed. However, several bullish factors associated with the halving have the potential to positively influence its value. Let’s delve deeper into these:
- The halving significantly reduces the flow of new bitcoins into circulation. This reinforces Bitcoin’s inherent scarcity, potentially making it more attractive to investors seeking assets with limited supply. In simpler terms, if fewer bitcoins are available, each bitcoin could become more valuable.
- The sudden decrease in new coin supply created by the halving could lead to a “supply shock.” This scenario occurs when demand for the existing, limited supply of bitcoins outpaces the supply. Imagine a scenario where everyone wants a slice of a smaller pie; the price of each slice would naturally tend to rise.
- With mining becoming less profitable due to the reward reduction, miners might be less inclined to sell their bitcoins. This further tightens the supply of readily available bitcoins, potentially pushing the price upwards.
However, it’s important to acknowledge the other side of the coin:
- The broader economic climate and overall sentiment towards cryptocurrencies can significantly impact Bitcoin’s price. Even if the halving does its part, a global economic downturn could be strong enough to mute any potential price surge.
- Stringent regulations or government crackdowns on cryptocurrencies could create uncertainty and scare away investors, potentially dampening any positive effects of the halving.
- If Bitcoin’s adoption as a mainstream medium of exchange or store of value starts to decline, the halving could have a muted impact on its price. Reduced usage could signify a decrease in overall demand for Bitcoin.
The Bitcoin halving is a significant event that injects a potent mix of anticipation and uncertainty into the cryptocurrency world. While a guaranteed price surge following the halving remains elusive, it is a stark reminder of Bitcoin’s core economic principles.
Beyond the Hype
The halving mechanism controls the issuance of new Bitcoin, mimicking precious metals like gold, and incentivizes efficient mining practices to ensure the network’s long-term security.
However, the impact of the halving on Bitcoin’s price is a complex issue. Historical data suggests potential price increases following previous halvings, but correlation doesn’t guarantee causation. Broader economic factors, regulatory landscapes, and Bitcoin’s overall adoption as a mainstream asset all play a role in determining its value.
The halving underscores Bitcoin’s potential for long-term growth beyond the immediate price implications. Its finite supply and the security measures woven into its design offer a compelling proposition for investors seeking a hedge against inflation and a store of value in the digital age.
Ultimately, approaching Bitcoin, or any cryptocurrency, requires a cautious and well-researched investment strategy. The halving serves as a valuable opportunity to revisit Bitcoin’s core functionalities and potential, but investors should be mindful of the inherent volatility associated with the cryptocurrency market.
By understanding the technical aspects of the halving and the broader economic landscape, investors can make informed decisions about their participation in this ever-evolving digital asset class.
On the Flipside
- As mining becomes less profitable due to the reward reduction, smaller miners may be squeezed out. This could lead to increased centralization of mining pools.
- The halving’s impact on price could diminish over time as Bitcoin matures. Adoption and regulation will likely play a larger role in future price movements.
- The halving has historically caused significant price swings in the lead-up and aftermath. This volatility can be risky for investors.
Why This Matters
The Bitcoin halving is a pivotal moment that alters Bitcoin’s core economics. By significantly reducing the new coin supply, it reinforces scarcity, potentially attracting investors seeking valuable assets. It could also trigger a surge in demand that outpaces supply, impacting the entire cryptocurrency market.
With the Bitcoin halving expected around April 20, some call for miners to slow production to align it with this culturally significant date. Read more here:
Bitcoin Miners Urged to Slow Production for 4/20 Halving
Analysts are looking at historical trends and technical indicators, suggesting a potential surge for XRP. But will history repeat itself? Find out here:
XRP Aims to Outshine BTC Post-Halving: Can It Repeat History?
