
- Blockchain is one of the most revolutionary inventions of the 21st century.
- It is a whole new technology, a decentralized database of immutable smart contracts, sequenced in blocks.
- Most popular blockchain use cases cover the sectors like:
- Finances
- Governance
- Healthcare
- Education
- Intellectual property
- Logistics
- Energy
- Real estate
The 21st century is remarkable for innovations and revolutionary inventions. However, one of the most fundamental ones is arguably the blockchain.
Within the last few decades technologies advanced at a phenomenal rate. Some of them play a critical role in revolutionizing economies and reshaping the future of nearly 7 billion people. Blockchain is such an invention. Decentralized technology has the power to impact any industry in the world and transform it. In this article, DailyCoin looks into the most common blockchain use cases and views how decentralized technology is going to shape the future of completely different sectors.
What is blockchain?
Technically, blockchain is an open-source digital ledger. A global decentralized database of enormous amounts of digital records. Or as the name says, a chain of blocks, that can record and store any type of structured information (transactions) in a way, when new confirmed blocks are constantly added to the existing ones.
The keyword here is decentralized. Blockchain is the underlying technology of any digital currency, but first, it is a distributed technology. It runs on millions of computers across the globe and stores all the information in a distributed manner.
Sponsored
It is open-source, so anyone can change its code, add and confirm data. This means all movements on the blockchain are Peer-to-Peer (P2P), with no third parties, intermediaries, or central authorities to affirm deals.
The decentralized nature enables blockchain technology to be truthful, immutable and transparent. As any transactions are recorded into blocks that are later added to the chain every 10 minutes (in Bitcoin’s blockchain case), it is almost impossible to forge and modify the stored data.
How does blockchain work?
The blockchain is an intelligent way of distributing information in a fully automated and safe way. To make it possible, blockchain uses smart contracts, the lines of code stored inside of the digital database.
Sponsored
Similarly to the physical contracts, smart contracts store the rules and conditions of the agreement in its algorithm, moreover they verify and execute the agreement if all terms and conditions are met.
The codes of smart contracts cannot be modified. This means, smart contracts are immutable and no one has the power to change the agreement and cheat. Moreover, due to the distributed nature of blockchain, all smart contracts are stored publicly what prevents them from any possible changes.
While physical contracts usually require a third party to confirm the deals and earn the commissions on it, blockchain also benefits the participant who confirms the transactions. The confirmation here is implemented by nodes, who solve the difficult mathematical puzzles. However, the nodes are run by miners – the people with computer hardware, that requires a lot of electric power to confirm these smart contract blocks.
Confirming these blocks means mining them or in simple words, adding the new blocks to the already existing chain. And as an intermediary in the real world gets the commission, the blockchain miners get a reward for their effort – the native cryptocurrency of the certain blockchain.
The blockchain use cases: how can it affect the industries
For the past few years, blockchain technology gained recognition across various industries that tend to benefit from decentralization. Multiple companies already create their own blockchains and digital currencies.
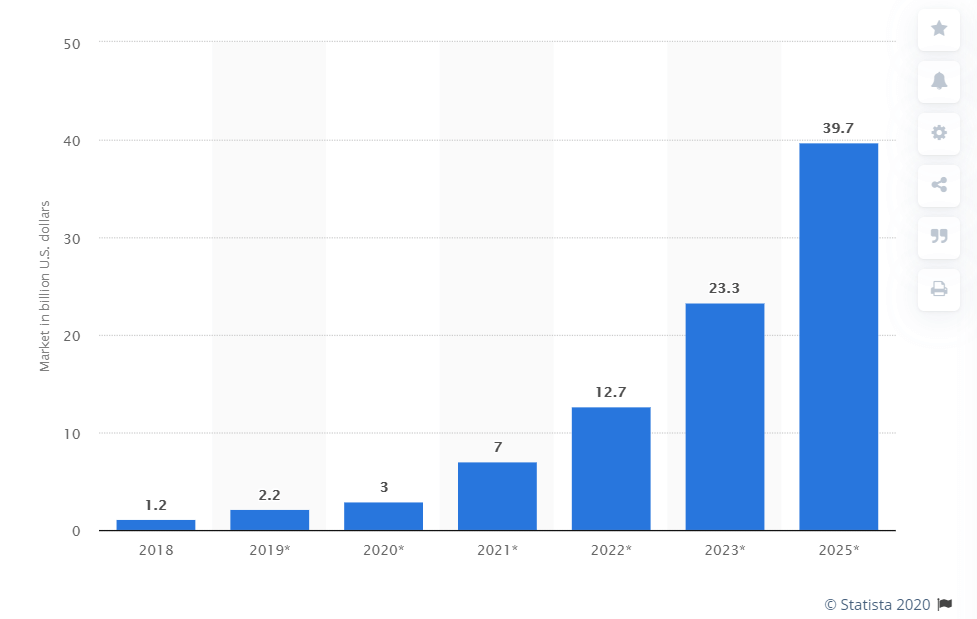
The size of the global blockchain technology market is expected to reach $39.7 billion by 2025. This is more than 13 folds more compared to 2020.
1. Financial sector
The financial sector is one of the pioneers in terms of blockchain adoption. The majority of technology market value is already settled in the financial industry. Decentralized technology has the potential to change multiple sectors including capital markets, bank and remittance services, and insurance.
Due to its decentralized nature, blockchain allows Peer to Peer (P2P) contracts and eliminates the intermediaries. Thus the most obvious changes blockchain can bring are cheaper and faster transactions. The same decentralization decreases the risk of human error and provides better integrity of the recorded data.
All records on a blockchain are stored and validated in a transparent and secure manner. Eliminating human errors also means higher transparency. This is critical to lowering the risks of money laundering, identity thefts, and other criminal financial activity.
2. Governance
Blockchain technology contains revolutionary solutions. And while it provides full transparency, it can act as an effective tool against corruption.
As a fully decentralized technology blockchain does not require intermediaries that can be bribed or affected by interested parties. Furthermore, all data (like usage of taxes) stored on immutable shared databases are secured from errors, modifications, and data erasures. They are always transparent and traceable. Anyone can track where their taxes are used, while trails can be used by law enforcement and government auditors.
Decentralized technology can also be used for blockchain voting and even for decision making. On a corporate scale, blockchain-based voting can help voters to engage more deeply in the decision-making process and even enable self-implementation processes when the result automatically take effect after the voting is finished.
3. Healthcare
Blockchain technology can make serious changes in the healthcare industry by shifting a focus from central authorities directly to patients. The decentralized technology eliminates the intermediaries that store patient’s medical records. This means doctors can easily access all the patient data since they don’t need to gather pieces of information from various sources.
Eliminating the intermediaries accordingly enhances the privacy and security of medical data. Any data recorded on the blockchain by the medical personnel cannot be modified until they reach the patient. Accordingly, immutable data prevents human errors that are critically important both in daily healthcare and in clinical trials.
Another issue is traceability. The pharmaceutical companies suffer million-dollar losses through medicines’ counterfeits, especially in developing countries. Blockchain technology helps to share information that includes proof of ownership and delivery records.
4. Education
In the academic world, all the student’s grades and other data has to be manually verified before issuing a certificate, diploma, or degree. This is a time-consuming and expensive process that requires accuracy and still has a high possibility of human error. Eliminating it helps to reduce management costs.
Although academic data is personal, it is still stored by third parties (universities or high schools). Blockchain can change the practice by giving data control to students as they get their academic data or documents issued and stored on the blockchain.
Another benefit blockchain can bring is the universally accepted standards. In case these standards are adopted, students do not need to translate and verify their diplomas when applying for a job in another country, which makes processes simple by reducing the bureaucracy.
5. Intellectual property (IP)
One of the biggest problems in the creative and innovation industries is the lack of a single verified global registry of works. There are many of them dispersed around the globe, with different protective laws being in force in separate jurisdictions. Such a situation often leaves IP owners unprotected globally.
Blockchain technology can make a difference in copyright protection. First of all, it can serve as an online intellectual property registry, where genuine authors and IP creators keep the certificates (proof of ownership) as well as any other data of how their intellectual property has been used.
Accordingly, the blockchain can be used as a virtual database to store the intellectual property itself and directly connect owners with their users. The direct link will also enable Peer to Peer (P2P) payments to authors, where both parties equally benefit, users pay less, and authors earn more as no intermediaries charge for their services.
6. Logistics
International trade is a highly digitalized business sector, however, the lower tiers of the supply chain still rely on slow manual processes. Such processing of critically important documents like bills of lading slows the process and makes it vulnerable to human errors or corruption.
Fully digitalized blockchain technology enables swift and accurate documentation. This also increases the efficiency of the supply chains and lowers unnecessary costs.
The lack of transparency and efficient traceability is a big issue in the shipping industry. Manufacturers still face their authorized product counterfeits. Meanwhile, immutable records on the blockchain enable transparent tracking of any product along its journey from manufacturer to the end-user. The ability to prove the origin of the product enables brand protection and even helps to save its reputation.
7. Energy sector
The energy industry is a playground of large players and fixed electric prices. Nevertheless, blockchain is already trying to decentralize it leading to higher energy autonomy and Peer to Peer (P2P) energy markets.
Blockchain technologies enable electricity autonomy and metering for households that can generate energy by themselves (e.g. by rooftop solar energy panels) and sell the excess energy to other participants in the Peer to Peer (P2P) energy market. The blockchain-based solution already successfully tested in Australia’s households solar energy trading.
Decentralized P2P energy markets bring benefits to small users as they reduce the control of the wholesale energy companies. Moreover, they liberalize electric energy prices, that respond to supply and demand laws and usually end to be lower than the fixed ones.
8. Real estate
Blockchain technology has already affected the real estate industry. First of all, a shared digital database of properties allows interaction with it in a fast, secure, and cost-effective way. The processes of property selling, buying, or renting are fully digitalized and more efficient. Reducing the number of intermediaries cuts the costs of transactions on real estate.
Additionally, the immutable nature of blockchain enables a higher transparency level within the real estate market. As it is impossible to hide the real value of the property transactions, blockchain technology might help to avoid tax evasion and even assist in fighting money laundering.
Nevertheless, the most revolutionary blockchain effect on the real estate industry is the real estate tokenization. Blockchain allows the purchasing and trading of tiny parts of certain property and makes the real estate industry more accessible to investors with small capital.
In summary
Decentralized technologies and immutable smart contracts are making blockchain a real game-changer, that already transforms numbers of industries. The innovative technology opens a lot of opportunities for progressive companies.
Various blockchain use cases reveal the benefits like greater transparency, secure management, and costs savings that the decentralization brings. Traceability of payments, tracking, and real-time data management enables the better prevention of financial frauds, helps companies to stay competitive and grow further.
