
Ethereum (ETH) is the second largest crypto by market capitalization, second only to Bitcoin (BTC). While Bitcoin is undeniably revolutionary, Ethereum has reimagined the real-world use cases of blockchain and cryptocurrency.
If Bitcoin lets you be your own bank, Ethereum takes things further. Fully decentralized and open-source, the Ethereum network aims to liberate millions of people worldwide from the grip of centralized entities.
Simple dApps within the ecosystem give you complete control of your assets and empower users to manage their finances through lending, borrowing, and trading. You can play engaging games and even collect provably unique digital art and store it on secure decentralized servers.
Sponsored
How does the Ethereum blockchain make all this possible? What exactly is a smart contract, and why are they so important?
Introducing Ethereum, the future of finance and the next generation of the internet.
About Ethereum
Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain network that gives users full custody of their assets and hosts apps, organizations, and peer-to-peer transactions on a publicly verifiable network. The Ethereum mainnet has no centralized owner. Instead, it’s governed by a community of users and powered by Ether, the native cryptocurrency of the network.
Sponsored
Anyone can build an application or use the network at any time. The Ethereum blockchain is permissionless, meaning that no centralized body can stop me if I want to send cryptocurrency to a friend, trade tokens on a decentralized exchange, or store data on-chain. Even the Ethereum Foundation, a non-profit that helps develop and guide Ethereum’s growth, doesn’t have the power to censor how the network is used.
Like Bitcoin, the Ethereum blockchain offers anonymity. No invasive KYC procedures need to be completed before using the network, and you don’t need to provide any personal details before storing your funds securely on-chain.
How does a network with no owner operate 24 hours a day, seven days a week, without interference or a centralized service managing everything?
How Does Ethereum Work?
The Ethereum network is a public blockchain supported by thousands of independent computers worldwide. Each participant is called a ‘Node’ and helps secure the Ethereum blockchain. This decentralized system is more stable and reliable than centralized systems because a single point of failure does not threaten it.
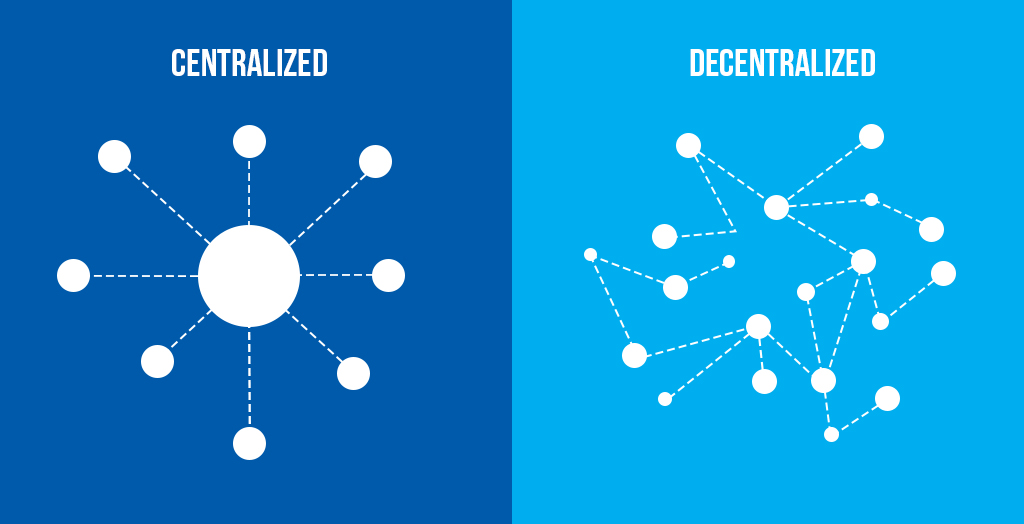
For example, take the diagram below. If the central piece of the centralized network suffers an outage, none of the other participants can communicate with each other. In a decentralized system, plenty of other interconnected nodes will step up and support the network if any nodes fail.
During The Merge, a network upgrade completed in September 2022, Ethereum migrated to a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. Ethereum’s PoS mechanism randomly selects validators to produce new blocks and secure the network. This is a more energy-efficient model than its original Proof-of-Work (PoW) mechanism, which demands high computational power.
Node operators are responsible for securing the Ethereum mainnet, processing transactions, and creating new blocks. As a reward for their services, these validators earn Ether tokens. Ether is valuable because users need it to pay transaction fees on the Ethereum network. However, ETH can also be sold on the crypto market in exchange for fiat currencies, like USD.
I know what you’re thinking; this sounds remarkably similar to Bitcoin or XRP. However, one key difference gives the Ethereum blockchain a greater variety of use cases than its predecessor.
Smart Contracts
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is a computational state that manages the network. Essentially, the environment houses all accounts and smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. Most Ethereum smart contracts are written in Solidity, the network’s dominant programming language.
Put simply, a smart contract is a line of code stored in blockchain programs and applications that execute when certain conditions are met. Smart contracts automate agreements between users in permissionless, anonymous environments, leading to greater trust and security on the network.
The easiest way to understand smart contracts is to imagine a vending machine. I enter an automated contract if I want a drink from the machine.
- I provide money and choose my drink, providing my side of our agreement.
- The vending machine accepts my money and automatically dispenses my drink, providing its side of our agreement.
Smart contracts allow Ethereum users to manage their cryptocurrencies more efficiently. They remove the need for intermediaries to oversee transactions. There is no room for human bias or error. Moreover, anyone can view the contract and verify its safety. In many ways, smart contracts add a layer of law and order to blockchain’s private and anonymous world.
Why is this important? What does Ethereum offer that traditional services cannot?
What Can I Do On The Ethereum Blockchain?
The Ethereum network is home to a rapidly expanding suite of apps and programs. Innovation and creativity are fully displayed in Web3, with new use cases being discovered and unveiled daily.
Decentralized Finance
First and foremost, the world of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is one of the most widespread use cases of the Ethereum blockchain. DeFi apps like Uniswap allow traders to swap ERC-20 crypto tokens with liquidity pools on-chain instantly. This not only gives traders access to a wider range of cryptocurrencies, but it also gives emerging Web3 startups a place to list their tokens without needing to pay a centralized exchange costly listing fees.
Lending and borrowing platforms like AAVE let DeFi users maximize their crypto holdings. In the same way, property owners can take out a loan against their house, apps like AAVE let holders get instant access to funds without selling their crypto. On the other hand, lenders can loan out their ETH and other cryptos to earn interest on their holdings in real-time.
Imagine trying to do any of this in traditional finance. Getting approved for a loan can take months and come with high fees from intermediaries like banks. Human bias also comes into play, and you have no way of knowing whether your loan will be approved. DeFi on Ethereum fixes this and levels the playing field. Anyone can access financial tools regardless of their funds, credit, or status.
NFTs
Non-fungible tokens have come a long way. While originally, NFTs were considered to be nothing more than flexes and digital art pieces, NFT utilities are evolving in earnest. Some of the world’s biggest brands, like Adidas and Porsche, are incorporating NFT technology into their businesses. TravelX, a Latin American travel company, is developing NFT flight ticketing services.
Ethereum is the home of NFT culture. The network allows anyone to mint an NFT, whether a document containing important information or a unique masterpiece of digital art. Creator royalties on NFT collections mean that artists will receive ongoing fair value for their work, even years after it was originally sold.
Data Storage & Decentralized Governance
Storing data on the Ethereum blockchain is a solution for users wanting decentralized and immutable storage options. Data stored on Ethereum is distributed across a network of computers, making it more resistant to hacking. Moreover, once data is stored on the Ethereum blockchain it’s immutable. It cannot be altered or deleted, providing a tamper-proof data record.
Ethereum data can be accessed and used by other decentralized applications within the ecosystem, enabling seamless integration between different Ethereum-based applications and programs.
By tokenizing assets on Ethereum, groups of individuals can form a DAO or a decentralized autonomous organization. Many decentralized platforms are governed by DAOs, who vote on development proposals and the community decisions that shape the protocol’s future.
Ethereum itself is governed in this way. Every decision that influences the future development of Ethereum is voted on by its community of Ether holders.
The Birth of Ethereum
The idea of Ethereum was first conceived by Vitalik Buterin when he was just a teenager. At the time, Buterin was a talented computer programmer and co-founder of Bitcoin Magazine. Buterin envisioned greater utility for blockchain technology beyond what Bitcoin could.

He published the first Ethereum whitepaper in 2014, which attracted the attention of other industry big brains like Gavin Wood and Charles Hoskinson.
In 2014, Buterin brought his idea for the world’s first smart contract-capable blockchain to the Bitcoin conference in Miami. The concept was met with enthusiasm, and the Ethereum founders hosted an ICO (initial coin offering), raising over $18 million in BTC.
The first iteration of the Ethereum mainnet, Frontier, officially went live in July 2015.
Ethereum 2.0 (Serenity)
While Ethereum is in itself a revolutionary technology, it is not without its flaws. Ethereum’s biggest issue is undoubtedly its scalability. The Ethereum network has congestion issues, like slow transaction speeds and high gas fees.
To address these problems, Vitalik and the Ethereum Foundation proposed a series of upgrades to the network. These Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) aim to reinvent the network into a more scalable and secure blockchain. While it’s most commonly referred to as ETH 2.0, the official name for the upgraded network is Ethereum Serenity.
There have been plenty of Ethereum upgrades over the years. However, the most important have been listed below.
Beacon Chain
Ethereum was originally a Proof-of-Work blockchain. Vitalik and the Ethereum Foundation proposed migrating to a Proof-of-Stake consensus to achieve true scalability and reduce energy consumption.
Following the approval of the proposal by the community, Vitalik, and the Ethereum foundation deployed the Beacon Chain in December 2020. Essentially, the Beacon Chain ran alongside the Ethereum main chain, testing how the PoS consensus would work within Ethereum’s infrastructure and laying a foundation for the Merge.
London Hard Fork (EIP 1559)
The London Hard Fork is a significant milestone for the Ethereum ecosystem. It introduced a deflationary mechanism that burned a small percentage of Ethereum transaction fees. This was introduced to counteract Ether’s inflationary validator rewards system.
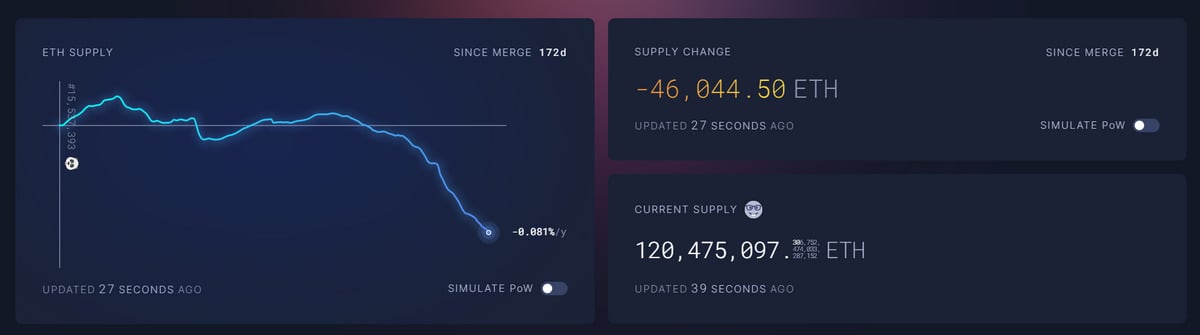
Source: UltraSoundMoney
Since the London Hard Fork, over 46,000 ETH has been burnt. This represents over $71 million at the current ETH price. Investors expect that the ongoing effects of the London upgrade will be positive for Ethereum price as the token supply becomes more scarce.
The Merge
Perhaps the biggest upgrade Ethereum ever witnessed occurred in September 2022. As the name would suggest, the Merge represented the key moment when Ethereum’s existing PoW chain merged with the Beacon Chain, Ethereum’s preparatory PoS chain.
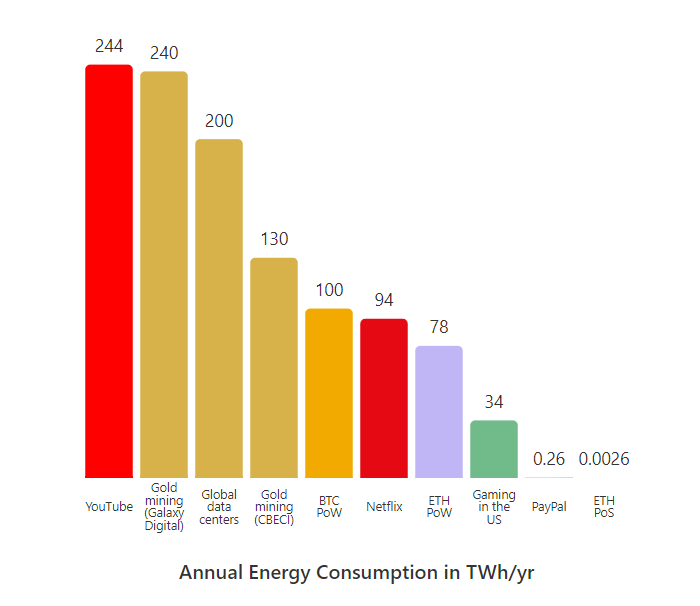
Source: Ethereum
Following The Merge, Ethereum became a far more energy-efficient network. The upgrade reduced Ethereum’s energy consumption by 99.95% and the earth’s total usage by around 1%. The transition to a PoS consensus has also enabled the network to implement Sharding, a scaling solution that will increase Ethereum’s transaction throughput and processing speeds.
Shanghai Upgrade (EIP 4985)
As part of the earlier Beacon Chain and Merge upgrades, Ethereum holders staked their ETH in locked contracts to help secure the network during the transition. Scheduled for early 2023, the Shanghai upgrade will release the staked ETH back to providers over time and aims to reduce transaction fees on the network.
It is expected that over 17 million ETH will be unlocked in the weeks following the Shanghai Hard Fork.
Dencun Upgrade
Considered the biggest upgrade to the Ethereum network in over a year, the Dencun Hardfork aims to reduce gas fees on Layer 2 networks like Polygon PoS (MATIC) and Arbitrum (ARB). The Dencun upgrade was officially finalized on March 13, 2024.
Theoretically, the hard fork enables ‘proto-danksharding’ on the network. Essentially, this provides new locations, called ‘blobs,’ solely dedicated to on-chain data storage. Accessing and conducting transactions through blobs requires lower gas fees than standard transactions.
Ethereum developers believe this update will lower gas fees associated with data storage, consequently reducing network congestion and improving Ethereum’s scalability.
Are Ethereum and Ethereum Classic the Same?
The short answer is no. Ethereum and Ethereum Classic are two completely separate blockchains. But the infamous DAO hack and the birth of Ethereum Classic have become integral parts of Ethereum’s history.
Back in Ethereum’s infancy, a group of passionate blockchain enthusiasts created ‘The DAO.’ The DAO was one of the first decentralized autonomous organizations in the crypto space and envisioned establishing itself as a decentralized venture capital firm that would become a key player in the industry.
After raising over $150M through an initial token sale, the DAO smart contract was hacked, resulting in over $60M worth of ETH being stolen. To alleviate the losses, the Ethereum community proposed a hard fork that would effectively ‘roll back’ the network and restart the chain from before the hack occurred.
The proposal caused waves of controversy and heightened tensions. Ultimately, the community decided that hard forking the network to its pre-hack state and resolving the security issue was in the best interest of Ethereum’s future.
This hard fork became the Ethereum we know and use today. The “original” network where the hacker retained the funds became Ethereum Classic and was largely discarded by the Ethereum community.
On The Flipside
- Since Ethereum first launched back in 2015, many other ‘Ethereum-Killer’ blockchains have emerged to compete with the market leader. These include popular networks like Cardano, BNB Chain, and Solana.
- While these competitors haven’t been able to reach ETH in terms of market cap, they have proven themselves as faster and more affordable alternatives.
Why You Should Care
Ethereum is the world’s first blockchain that supports smart contracts and introduced concepts like DeFi and NFTs to the masses. It’s by far the most adopted Layer 1 blockchain in the industry.
FAQs
You can buy Ethereum on crypto exchanges like Binance, Coinbase, or Kraken. Please ensure that regulators permit your purchase in your local jurisdiction.
Ethereum is a blockchain network used to build decentralized applications, store data, and information, and manage personal digital assets. Its native token, Ether, is used to pay transaction fees on the network and is always used as a currency of exchange for goods and services.
Ethereum is fully decentralized and censorship-resistant, meaning it’s accessible to users worldwide. Through smart contracts, people can access financial tools and services they might otherwise not have access to.
How long you hold Ethereum is a personal decision based on your investment thesis. We recommend you conduct thorough research before investing in any cryptocurrency.
Cryptocurrencies like Ethereum are high-risk assets prone to unexpected price volatility. Whether or not Ethereum is a good price to buy right now depends on your investment strategy. As a rule of thumb, we recommend never investing more than you can afford to lose.
