
Bitcoin (BTC) has been given plenty of names in its lifetime. Digital Gold, The Future of Money, even ‘The Biggest Ponzi Scheme in Human History.’ Over a decade has passed since Satoshi Nakamoto published the Bitcoin Whitepaper. Despite bitcoin price volatility and what its naysayers would have you believe, Bitcoin is here to stay.
Not only has Bitcoin stood the test of time, the world’s largest digital asset also inspired a technological revolution. Cryptocurrency and blockchain technology are re-inventing how we store our funds and manage our finances online in a way that traditional systems, like central banks, cannot replicate.
Decentralized and fully open-source, the bitcoin network has given people greater control over their finances than ever before. It blazed the trail for other digital currencies, like Ethereum (ETH) and Ripple (XRP), to innovate and improve. While it’s more often considered a store of value than a currency these days, Bitcoin is still the centerpiece of the crypto market.
Sponsored
What is Bitcoin? What is bitcoin mining and Proof-of-Work? Will Bitcoin always be king, or is it possible that altcoins like Ether or BNB will siphon BTC’s market cap and take its place at the top?
What Is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency, a kind of digital asset that’s used in the same way as fiat currencies like USD. With BTC, users can pay for goods and services and send funds to friends and family using a decentralized, peer-to-peer network.
Sounds like normal money, right?
Sponsored
Not really.
Fiat currencies, such as the USD or EUR, are controlled and governed by centralized bodies. They’re often stored in central banks that can deny users access to their funds. If I want to transfer fiat currency to someone, I must trust an intermediary to settle the payment. This third party could block the transfer or charge me extortionate fees for their services.

On the other hand, bitcoin transactions are trustless and permissionless. Nothing stops me from using the bitcoin blockchain and sending BTC directly to a friend or business over the network. Moreover, I can watch the transaction in real-time by tracking it transparently on-chain.
How does it all work, then? If there’s no intermediary to settle the payment, what ensures that bitcoin transactions are processed?
How Does Bitcoin Work?
The bitcoin network is powered by miners and a unique algorithm called the Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism. Bitcoin miners are responsible for processing transactions on the blockchain and producing, or ‘mining’ new blocks. Simply put, a block is a unit of data on the blockchain that records previous transactions.
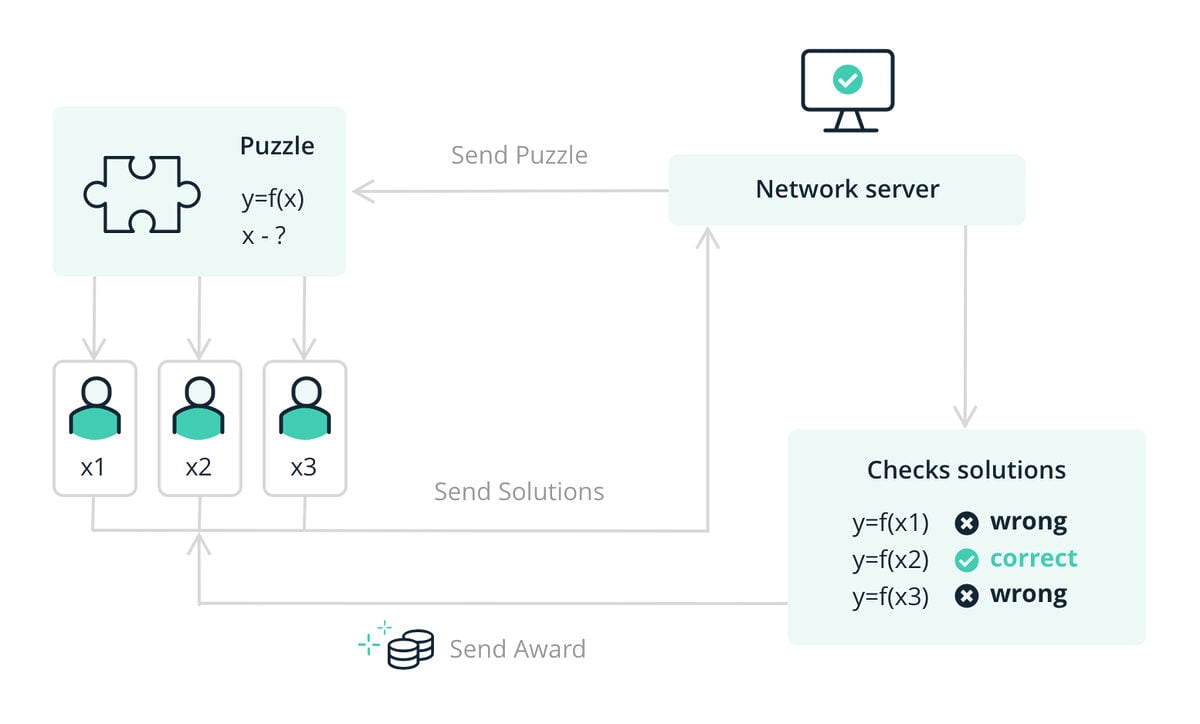
In the Proof-of-Work mechanism, miners compete to produce new blocks. Using intensive computational power, Miners solve complex puzzles using cryptography. Miners earn BTC as a reward for solving these puzzles, which process bitcoin transactions and create new blocks for the network.
Another thing separating Bitcoin from traditional fiat currencies is that BTC has a fixed max supply of 21 million coins. This makes BTC immune to inflation and is one of the main reasons many investors consider BTC a store of value and a hedge against inflation.
Bitcoin miner rewards slowly diminish over time through a process called Bitcoin halving. After every 210,000 blocks, the amount of BTC distributed to miners is cut in half. When BTC was first launched in 2009, every new block released 50 BTC into the circulating supply. However, following the third halving in May 2020, these rewards have been reduced to just 6.25 BTC per block.
What Can Bitcoin Be Used for?
The bitcoin network was originally designed to be a decentralized peer-to-peer payment network. As a result, it’s most commonly used to send and receive funds anonymously over the internet. However, BTC has grown beyond its initial use cases and is now considered a store of value, like gold. This makes it a popular investment vehicle for speculators.
As blockchain technology evolves, BTC is witnessing greater adoption and utility. El Salvador recognizes BTC as a legal tender, and businesses worldwide accept bitcoin payments in exchange for goods and services. Even publicly traded, NASDAQ-listed companies like Tesla hold BTC, and other altcoins like DOGE, on their balance sheets.
What’s more, innovation across the cryptocurrency industry continues to bring further use cases to Bitcoin. For example, BTC can be wrapped and deployed onto other blockchain ecosystems. This means that bitcoin’s value and liquidity can be used in DeFi apps on Ethereum.
With the rise of Ordinals, the Bitcoin blockchain hosts its own NFTs. These ordinal NFTs exist on the Bitcoin network, denominating their value in BTC price. At the beginning of 2023, Ordinal trading volume brought renewed attention and fresh eyes to the world’s first cryptocurrency.
Bitcoin Pros & Cons
Objectively, Bitcoin is far from perfect. While it provides a secure, transparent, and decentralized payment network available to anyone with an internet connection, the bitcoin blockchain still has drawbacks.
Bitcoin Pros
- Decentralized – The bitcoin network has no centralized owner or governance. Moreover, the blockchain is distributed, meaning the network will remain fully functional even if large mining operations unexpectedly collapse.
- Fast – Bitcoin transactions are faster than traditional banking transfers and are not restricted by international borders. With bitcoin, you can send funds anywhere in the world in seconds.
- Accessible – Anyone with access to the internet can own bitcoin and use it for payments. There are no invasive KYC procedures that might stop users from opening a bank account or accessing financial services.
- Affordable – Bitcoin transactions cost anywhere between a few cents and a couple of dollars, dependent on network congestion. In a world where centralized banks can charge commissions on large transfers and international transactions, the bitcoin network is an affordable option.
- Transparent – The Bitcoin blockchain is a transparent and publically verifiable ledger of transactions. The entire protocol is open-source, meaning anyone can verify its source code to ensure the network is safe.
Bitcoin Cons
- Energy Consumption – One of bitcoin’s biggest criticisms is that it requires enormous computational power. Analysts like the Bitcoin Energy Consumption Index estimate that over a year, the bitcoin network uses as much energy as Kazakhstan and expels a carbon footprint comparable to Portugal.
- Scalability Issues – While the Bitcoin blockchain is faster and more affordable than traditional banking, competing blockchain payment networks like Ripple have developed far more scalable systems. While Bitcoin processes around 4-5 transactions per second, Ripple handles over 1,000, with reduced fees.
- Price Volatility – If you’ve spent time in the crypto market, you’ll understand that bitcoin prices are prone to unexpected drops and surges. These prices affect Bitcoin’s market capitalization, and this volatility makes it difficult to use BTC as a currency of exchange.
Bitcoin’s Mysterious Beginnings
The Global Financial Crisis of 2008 wreaked havoc on economies worldwide. Central banks and financial institutions were in critical debt after a sudden housing market crash destroyed the value of their assets. Governments were forced to bail out overleveraged banks and institutions, and the resulting credit crunch broke the global economy.
In 2008, Bitcoin’s anonymous founder, or group of founders, published the Bitcoin whitepaper. Satoshi Nakamoto’s iconic document has become a manifesto for crypto enthusiasts. In just a few months, the Bitcoin network was launched. Nakamoto themself mined the first block, immortalizing a significant line of text into the blockchain forever: “The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks.”
Satoshi Nakamoto continued to contribute to the bitcoin project. However, in 2011 the enigmatic founder confirmed in an email to a friend that he’d moved on from Bitcoin. He remains anonymous, though it is widely accepted he is the world’s largest BTC holder.
The Future of Bitcoin
Despite Nakamoto’s disappearance, the bitcoin community has continued to develop the network to keep up with the growth of the wider blockchain industry. Their primary adjective is to increase the network’s scalability without sacrificing its decentralization.
With the uprising of smart contracts and decentralized finance, parts of the bitcoin community are worried that the network will get left behind. Some developers are working towards deploying native bitcoin smart contracts in the ecosystem, which will provide greater utility to BTC moving forward.
Lightning Network
Initially proposed in 2015, the Lightning network is a kind of Layer 2 scaling solution for Bitcoin transactions. It takes certain payments off-chain into specific channels between two trusted parties. The Lightning network is intended for smaller, everyday transactions like buying coffee. As the name would suggest, the Lightning network is faster and more affordable than Bitcoin’s main network.
Bitcoin Smart Contracts – TapRoot Upgrades & Stacks Network
Recent Taproot upgrades have introduced basic payment smart contracts to the network to make Bitcoin more composable. However, given Bitcoin’s underlying immutable code, these contracts are rather limited and don’t come close to the flexibility provided by other Layer 1 networks like Ethereum.
Meanwhile, the Stacks (STX) network is an open-source Layer-1 blockchain that connects to Bitcoin’s main chain. Stacks provide developers and users with a suitable environment to deploy more complex smart contracts. The project aims to bring smart contracts to the Bitcoin ecosystem while utilizing Bitcoin’s security.
In the same way that BTC can be wrapped and deployed on Ethereum as wBTC tokens, Stacks will host sBTC tokens that can be redeemed for BTC at a 1:1 ratio.
On the Flipside
- Despite providing the foundation for the entire cryptocurrency and blockchain industry, Bitcoin’s scalability issues make it difficult to use as a payment network. Bitcoin also devastates the environment and consumes as much energy per year as a small country.
Why You Should Care
Without Bitcoin, your favorite blockchain, NFT, or meme coin wouldn’t exist. It’s important to know why Bitcoin and blockchain technologies were created and how they work. This also extends to the value of true decentralization and self-custody, which are cornerstones of the cryptocurrency world.
FAQs
You can buy bitcoin on almost every crypto exchange, such as Coinbase or Binance. Alternatively, you can try mining bitcoin if you want to acquire BTC without buying it.
Bitcoin’s all-time high price was recorded on November 10, 2021. The price of Bitcoin was $68,789.
Most crypto enthusiasts believe that Satoshi Nakamoto, the founder of Bitcoin, holds the most BTC. The anonymous enigma is estimated to hold over one million coins.
Like all cryptocurrencies, Bitcoin is a high-risk digital asset. We recommend that you always do thorough research and formulate your own investment thesis before buying BTC, and never invest more than you can afford to lose.
In most cases, you must pay taxes on your bitcoin transactions. Please refer to our helpful guide on crypto taxes for more information.
